Figure 3. WDR5 regulates dendritic polarity of cortical pyramidal neurons.
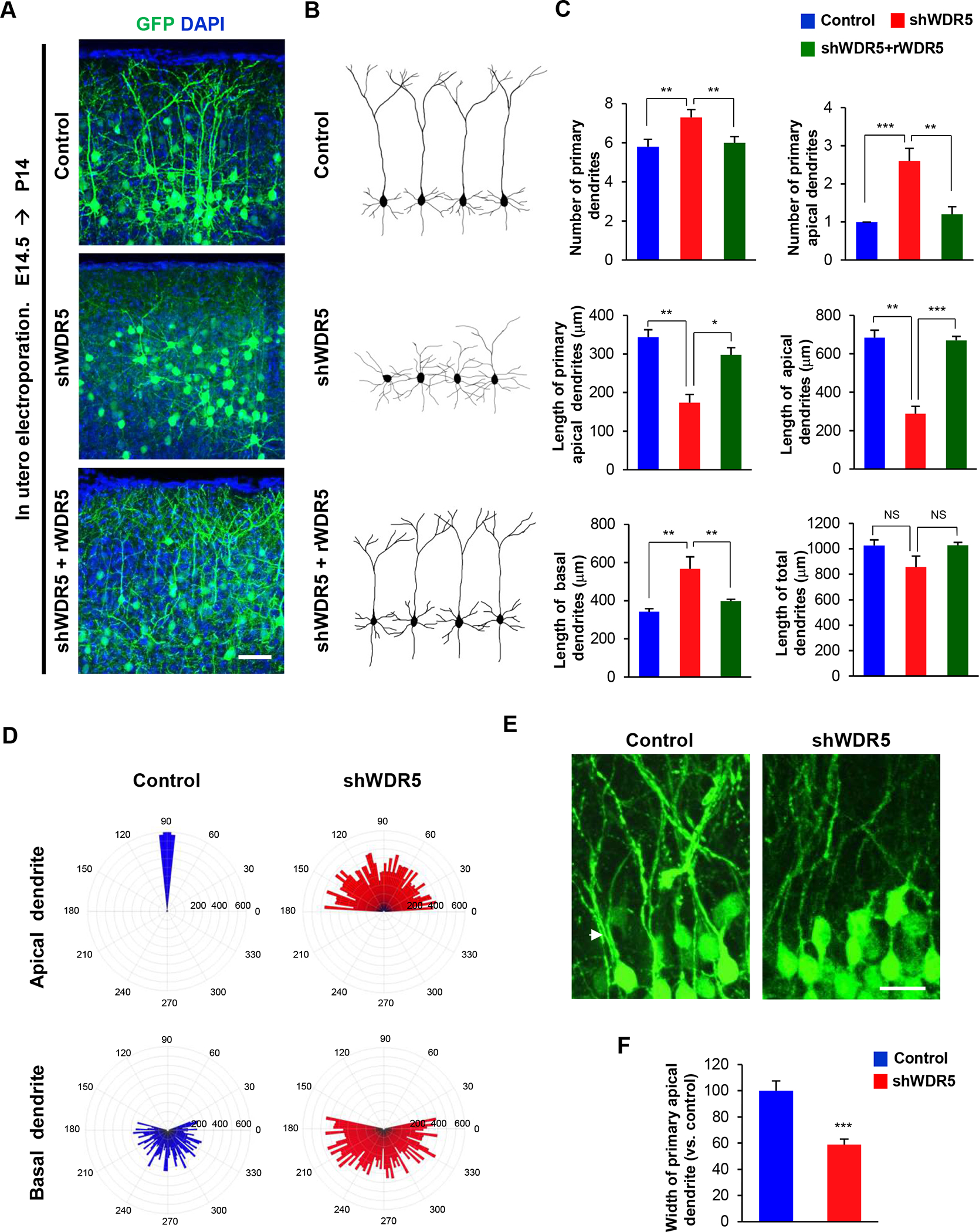
(A) Knockdown of WDR5 inhibits primary apical dendrite development in pyramidal neurons, and co-expression of rWDR5 construct restored the inhibitory effect of shWDR5. E14.5 embryos were electroporated in utero with a control or shWDR5 or shWDR5 and rWDR5 construct to target cortical pyramidal neurons. The electroporated brains were collected at age P14 and dendrite morphologies in pyramidal neurons expressing GFP were visualized. Scale bar, 25μm. (B) Representative morphologies of control, shWDR5 or shWDR5 + rWDR5-expressing pyramidal neurons with their dendrite formation. (C) The numbers and lengths of dendrites were quantified. n=5 mice for each condition. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferonni correction test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (D) Knockdown of WDR5 shows abnormal orientation of apical dendrites in pyramidal neurons. The numbers on the outer circle indicate the degrees of angles from the right horizontal line. The numbers inside of the outer circle show the lengths of dendrites. n=50 cells from 5 mice for each condition. (E) Knockdown of WDR5 shows thin primary apical dendrite in pyramidal neurons. Arrowheads show the primary apical dendrite of pyramidal neurons. Scale bar, 10μm. (F) The width of main apical dendrites was quantified. n=5 mice for each condition. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. ***p < 0.001.
