FIGURE 1. Results from quantile g-computational BTEX-H mixture analysis with asthma risk.
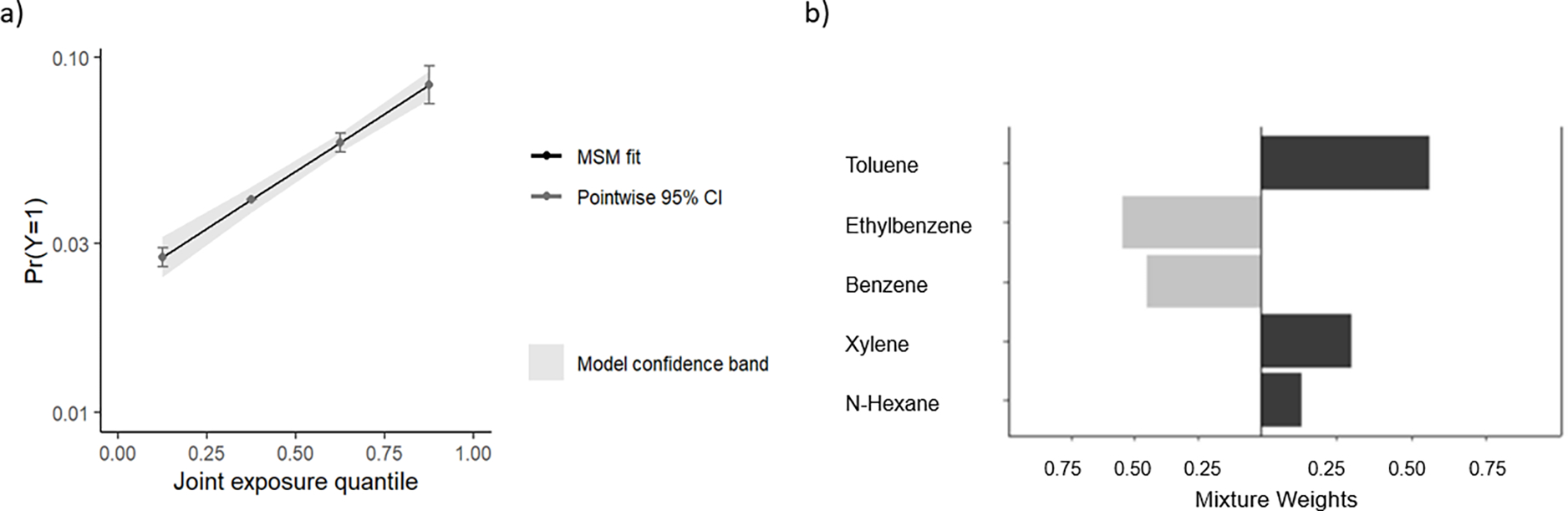
a) Shows the marginal structural model (MSM) fit (dark gray) for the association between increasing mixture exposure quartiles and asthma risk. The x-axis represents quartiles of the BTEX-H mixture and the y-axis represents the log odds of asthma. b) Weight representing contribution to the mixture effect of each chemical component. When all components are considered together, the relative contribution of toluene, xylene, and n-hexane have the greatest contribution to the mixture effect. Coefficients for each chemical component from the underlying model are as follows: Benzene (Beta:−0.07, SE:0.08, p-value:0.36), Toluene (Beta:0.34, SE:0.08, p-value:1.60 × 10−5), Ethylbenzene (Beta:−0.11, SE:0.09, p-value: 0.23), Xylene (Beta:0.19, SE:0.08, p-value:0.02), n-Hexane (Beta:0.08, SE:0.06, p-value:0.20).
