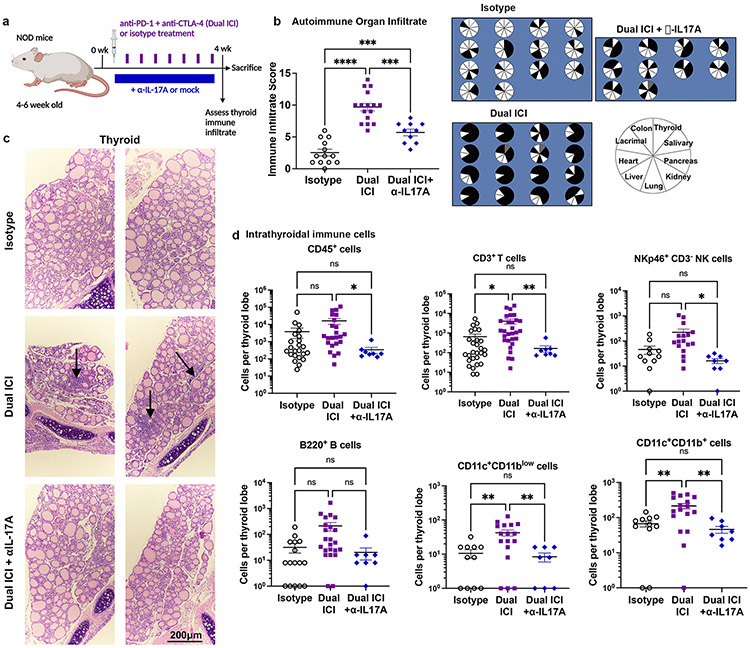
Figure 4. Neutralizing interleukin (IL)-17A antibody therapy reduces ICI-associated thyroid autoimmune infiltrates.
a, Schematic of treatment regimen combining anti-PD-1 + anti-CTLA-4 (Dual ICI) with a neutralizing IL-17A antibody (αIL-17A) in NOD mice. b, Autoimmune organ infiltrate score after 4 weeks of ICI treatment in isotype (n=14), Dual ICI (n=16), or Dual ICI + αIL-17A (n=10). Pie charts (right) showing tissues with immune infiltration after 4 weeks of ICI treatment. Each pie represents one animal; black = immune infiltrate, white = no infiltrate, gray = no data. c, Representative H&E micrographs of thyroid immune infiltrates in isotype (top), Dual ICI (middle), or Dual ICI + αIL-17A (bottom) treated mice (original mag. 400x). Arrows indicate areas of focal infiltrates. d, Intrathyroidal immune cell frequency among groups [isotype, n=11, except n=16 for CD3+), Dual ICI (n=17, except n=23 for CD3+), Dual ICI + αIL-17A (n=8)]. Data are mean ±SEM shown. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Brown-Forsythe ANOVA, assuming unequal s.d., followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (b, d).