Fig. 3.
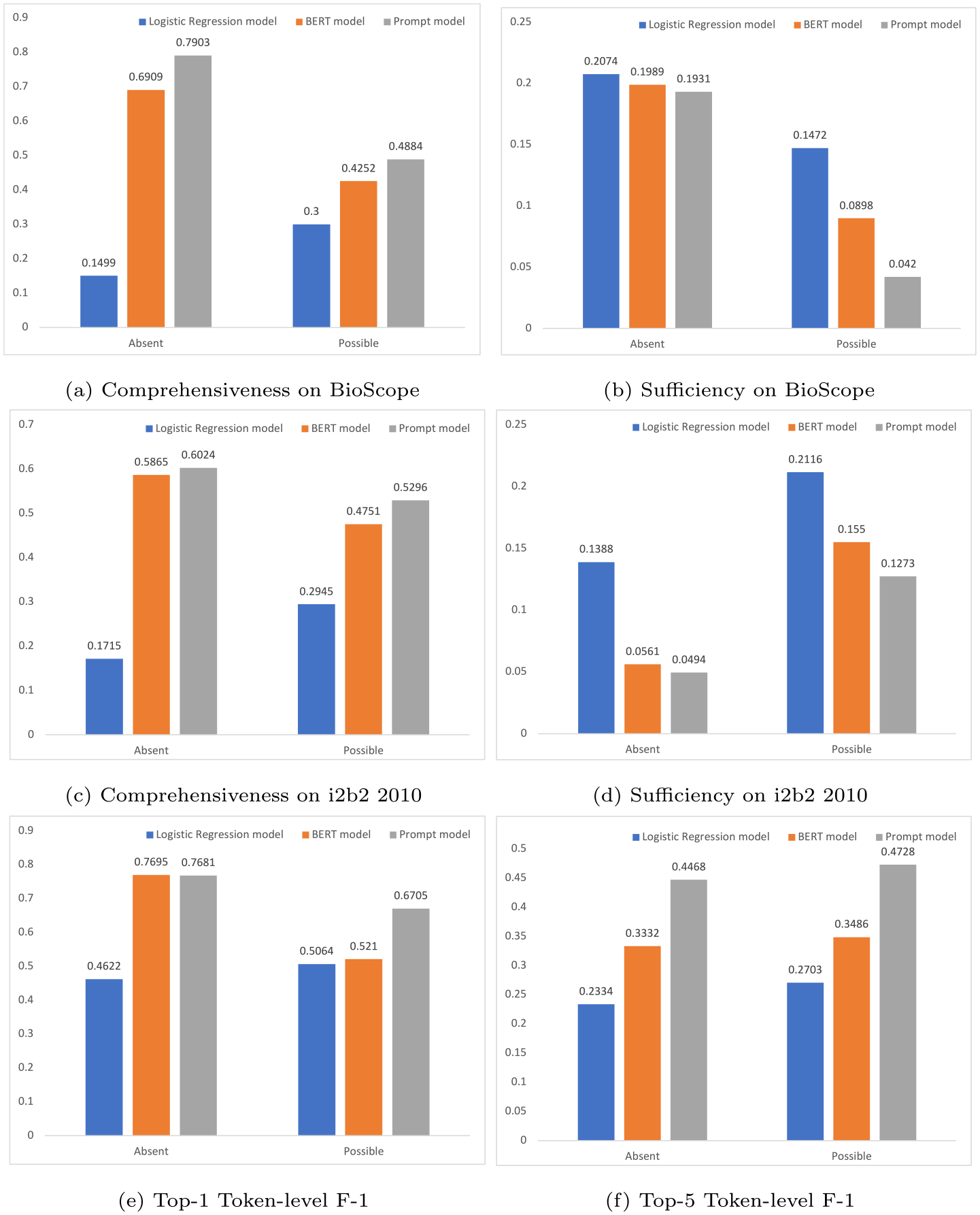
Comparisons of model rationality. (a) comprehensiveness comparisons on BioScope. A higher comprehensiveness score implies a more important role the linguistic cues play in the model’s prediction. (b) sufficiency comparisons on BioScope. A lower sufficiency score implies the model’s better capability of capturing sufficient features. (c) comprehensiveness comparisons on i2b2 2010. (d) sufficiency comparisons on i2b2 2010. (e) Top-1 token-level F-1 comparisons on BioScope. A higher score implies the highest-scored model rationale token has a better agreement with the ground truth rationales. (f) Top-5 token-level F-1 comparisons on BioScope. A higher score implies that the top-5 model rationale tokens are better aligned with the ground truth rationales.
