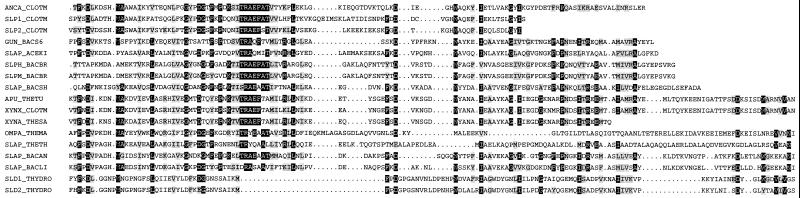
FIG. 2.
Alignment of the two Th-APu SLDs with a variety of eubacterial SLDs. The alignment is based on ProDom domain 1624 (INRA, Toulouse, France), which was constructed from 15 eubacterial sequences aligned with the MultiAlin alignment tool. The proteins used to define ProDom 1624 are as follows: ANCA_CLOTM, cellulosome anchoring protein from C. thermocellum; SLP1_CLOTM and SLP2_CLOTM, SLPs from C. thermocellum; GUN_BACS6, endoglucanase from Bacillus sp. strain KSM-635; SLAP_ACEKI, S-layer glycoprotein from A. kivui; SLPH_BACBR, SLP from Bacillus brevis; SLPM_BACBR, middle cell wall protein from B. brevis; APU_THETU, type II pullulanase from T. thermosulfurigenes; XYNX_CLOTM, exoglucanase from C. thermocellum; XYNA_THESA, endoxylanase A from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum; SLAP_BACSH, SLP from Bacillus sphaericus; OMPA_THEMA, outer membrane protein A from Thermotoga maritima; SLAP_THETH, SLP from Thermoanaerobacterium ethanolicus; SLAP_BACAN, SLP protein from Bacillus anthracis; SLAP_BACLI, SLP from Bacillus licheniformis. The Th-APu sequences were manually fitted to the ProDom alignment by introducing uniform gaps where necessary. White characters on a black background indicate areas where sequence identity is equal to or greater than 50%, while gray shading indicates areas where sequence similarity is equal to or greater than 50%. The groups of similar residues were considered to be I, L, V, M; D, E; N, Q; S, T; R, K; and F, Y, W. Dots indicate gaps in the sequences. SLD1_THYDRO and SLD2_THYDRO are the two Th-Apu SLDs.