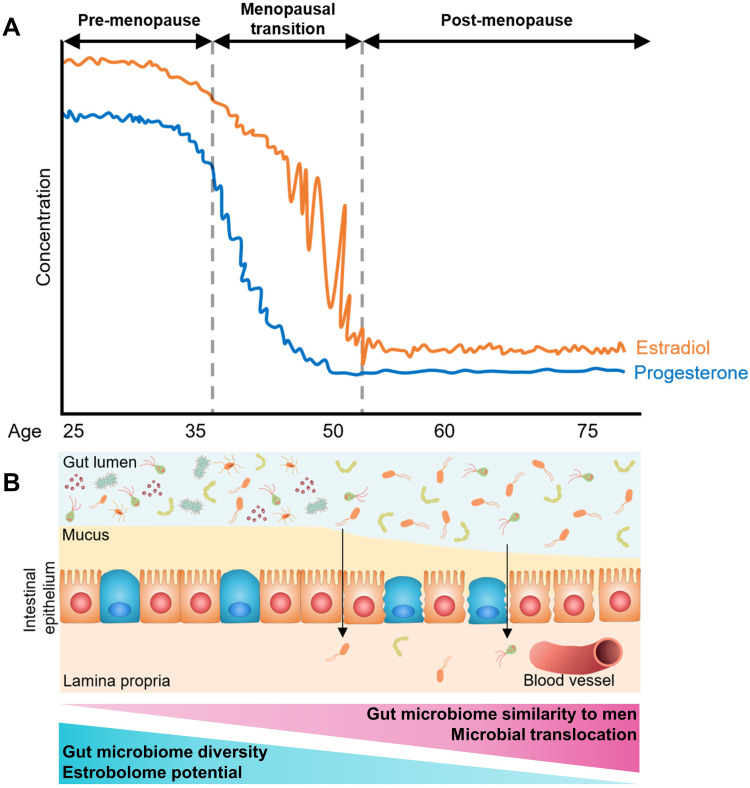
Figure 2.
Summary of putative changes in the human gut microbiome related to menopause. (A) Trajectory of estradiol and progesterone concentration during a woman’s adulthood, showing declines during the menopausal transition and low levels post-menopause. (B) Diagram of putative gut microbiome and gut epithelium changes during menopause. With declining estradiol and progesterone, diversity of the gut microbiome and estrobolome potential is reduced, and microbiome composition becomes more similar to men. Additionally, declines in estradiol and progesterone may lead to permeability of the gut barrier, allowing microbial translocation to occur.