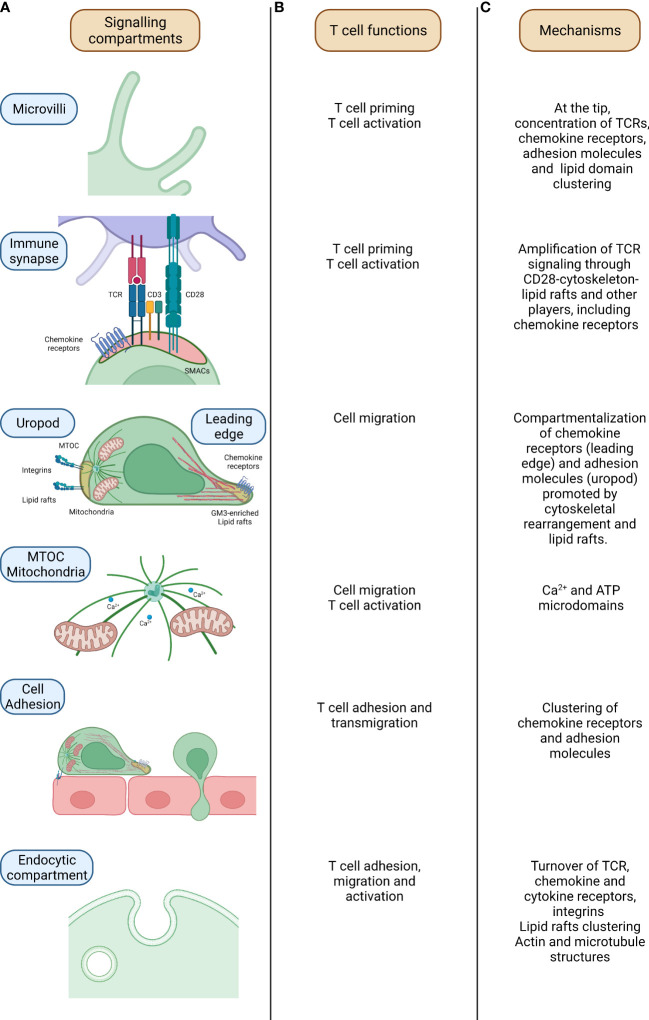
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of signalling compartmentalization in T cells. From the left, relevant compartments which regulate signalling compartmentalization in T cells (A), related T cell activities (B) and mechanisms underpinning signalling compartmentalization at these sites are outlined (C). In microvilli, parallel actin filaments allow the sustainment of the structure which assure the concentration of proteins and molecules and signalling compartmentalization in naïve T cells. In the immune synapse (IS), where the formation of the couple between the T cell and the APC is assured by the specific recognition of the Ag recognized on the MHCII molecules by the TCR, the binding of the two cells is further sustained by the CD3 and co-stimulatory molecules (CD28/B7-1/CD80-B7-2/CD86). Here, the compartmentalization of the signalling is mediated by the concerted action of cytoskeletal components, lipid rafts and endocytic compartment. During T cell migration, the T cell acquires an intrinsic polarity mandatory for the definition of a leading edge and a rear pole (uropod). The differential segregation of proteins at these two poles (cytokines and chemokines receptors at the front side while mitochondria and integrins of the rear one) assures the functional motility of the T cell. Mitochondria relocation within the T cell is mediated by microtubules in a Ca2+ dependent fashion. This process is orchestrated by the MTOC (microtubules organizing center) which controls microtubules polymerization and then mitochondria localization in a Ca2+ -dependent fashion. The definition of T cell polarity is mandatory for a proficient T cell migration with, on one side, chemokine receptors guiding the movement at the leading edge while, on the other side, adhesion molecules controlling T cell adhesion hence providing an antithetic force. Lastly, the endocytic compartment, apart from the recycling of molecules, promotes the fine compartmentalization and the amplification of the signal with the juxtapositioning of molecules and proteins. TCR-T cell receptor; MTOC-MicroTubule Organizing Center; ATP-Adenosine TriPhosphate.