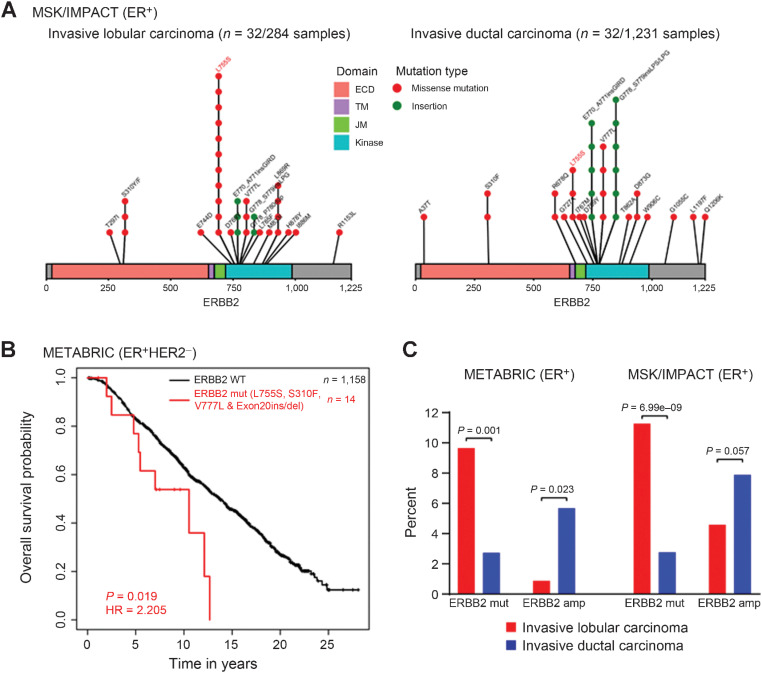
Figure 1.
HER2 mutations are significantly enriched in ILC as compared with IDC, in ER+ primary and metastatic breast cancer. A, Lolliplot showing HER2 mutations identified from the MSK/IMPACT data set in ER+/ILC and IDC. Three HER2-mutant patient samples (T297I, L755S, and L869R) harbor co-occurring HER2 amplification in ILC. Five HER2-mutant patient samples (E770_A771insGIRD, R678Q, V777L, V777L, and A37T) harbor co-occurring HER2 amplification in IDC. Two patient samples in ILC have more than one co-occurring mutation. One patient sample in IDC has more than one co-occurring mutation. B, Kaplan–Meier curves showing OS analysis of recurrent selected HER2 mutations (L755S, S310F, V777L, and Exon 20ins/del) in the ER+ and HER2 nonamplified subsets of the METABRIC cohort. P value determined by the Wald test. HR, hazard ratio. C, The prevalence of HER2 mutations was examined in ILC and IDC using primary (METABRIC) and metastatic (MSK-IMPACT) ER+ sequencing studies. The ILC subset shows 9.65% (METABRIC) and 11.27% (MSK/IMPACT) prevalence as opposed to 2.73% (METABRIC) and 2.60% (MSK/IMPACT) in the IDC subset. In addition, the prevalence of HER2 amplification was examined in ER+ ILC and IDC cohorts. The ILC subset shows 0.87% (METABRIC) and 4.58% (MSK/IMPACT) prevalence as opposed to 5.68% (METABRIC) and 7.88% (MSK/IMPACT) in the IDC subset.