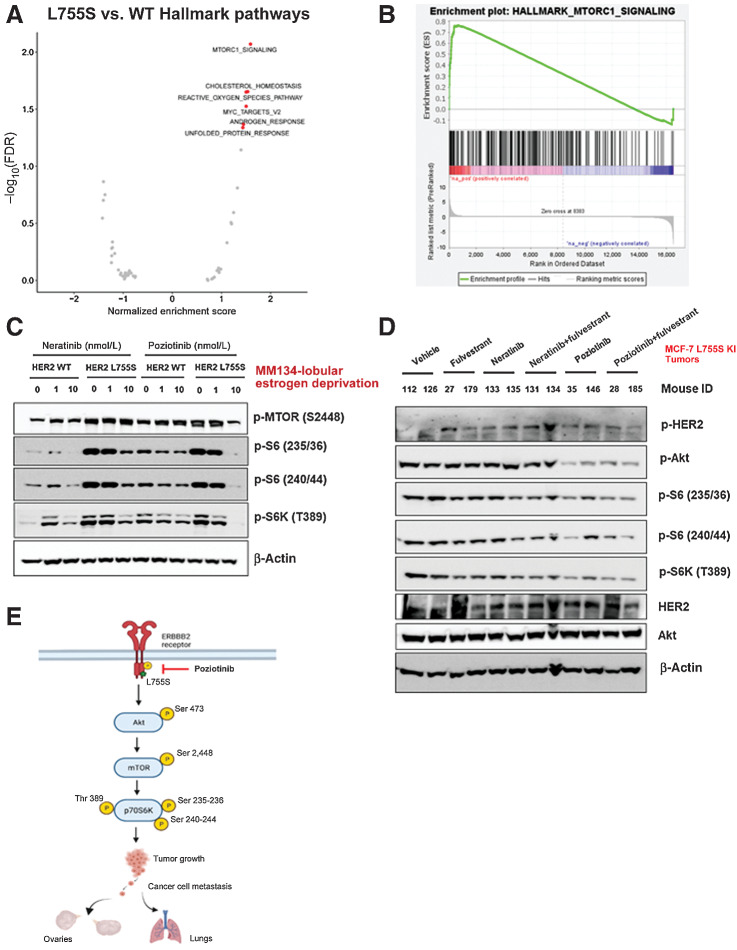
Figure 5.
HER2 mutations activate the HER2–mTOR signaling axis and may be associated with neratinib or fulvestrant resistance, yet poziotinib treatment alone inhibits the HER2–mTOR signaling axis. A, MM134 HER2 WT or L755S cells were grown in low-estrogen conditions and subjected to RNA sequencing analysis. GSEA of the top upregulated and downregulated genes in L755S cells as compared with HER2 WT cells identified the mTOR signaling pathway as the most significantly enriched pathway in L755S cells. B, Gene enrichment pathway analysis of RNA sequencing data from A was performed. Normalized enrichment score (NES) for the mTOR pathway is 1.59 and false discovery rate q value is 0.009. C, MM134 HER2 WT or L755S cells grown in low-estrogen conditions were treated with neratinib or poziotinib for 4 hours at the indicated concentrations. The cells were harvested and protein lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis for phospho-mTOR and its downstream substrate phospho-S6; protein expression. D, MCF7-L755S KI tumors were harvested from Fig. 4B, and protein lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for phospho-HER2, phospho-Akt, phospho-mTOR, and phospho-S6 protein expression. E, Schematic representation of mechanistic link describing poziotinib efficacy in inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis.