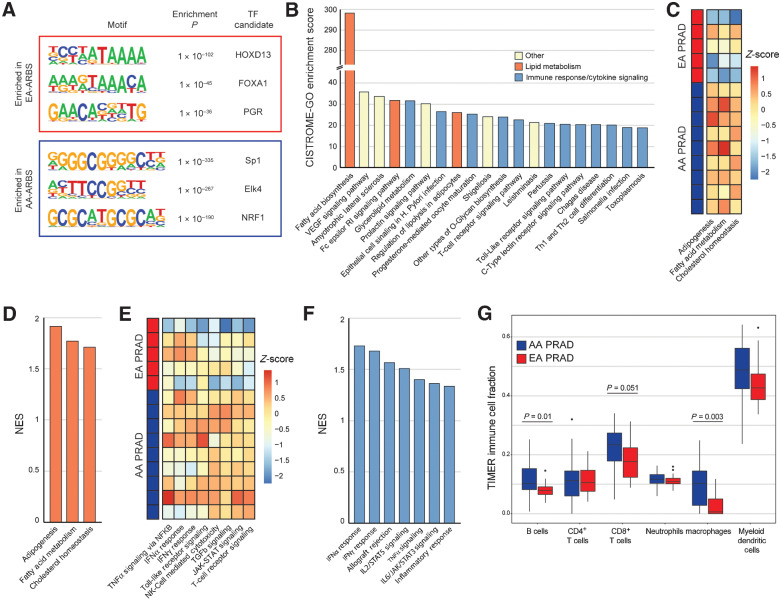
Figure 3.
The AR prostate cancer cistrome associates with lipid metabolism, immune response, and cytokine signaling. A, Three most significantly enriched nucleotide motifs present in AA-ARBS and EA-ARBS by de novo motif analysis. B, Pathway enrichment of the AA-ARBS identified using CISTROME-GO (23). C and E, AR binding intensity in each AA and EA prostate tumor for Hallmark lipid metabolism (C) and immune response and cytokine signaling (E) gene sets using ssGSEA analysis (24). D and F, Differential expression analysis in our RNA-seq data identifies upregulation of Hallmark lipid metabolism (D) and immune response and cytokine signaling (F) gene sets in AA (n = 30) versus EA (n = 19) prostate tumors. G, Estimation of tumor infiltrate immune populations demonstrates greater signal for B cells (P = 0.01) and macrophages (P = 0.003), and a trend towards CD8+ T cells (P = 0.051) in AA versus EA prostate cancer (41). NK, natural killer.