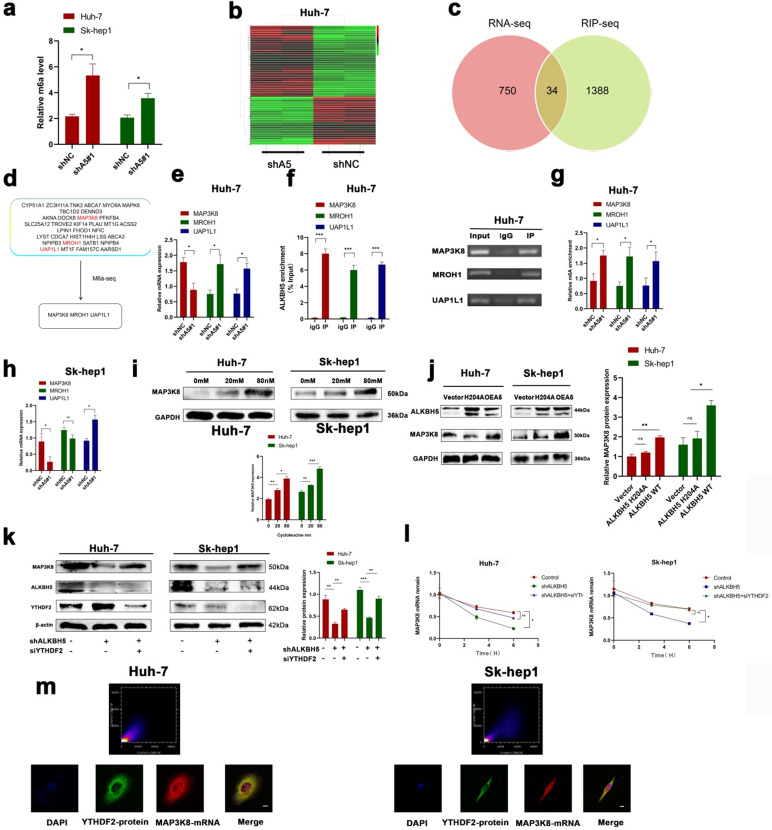
Figure 4.
ALKBH5 regulates MAP3K8 in an m6A -dependent manner. (a) The overall level of m6A changed after intervention of ALKBH5 expression by m6A colorimetry. (b) RNA-seq for HUH-7 cells with or without ALKBH5 knockdown n=2. (c) Intersection of the mRNA-seq and RIP-seq datasets (ALKBH5 binding target genes) (GSE144963). (d) Intersection of the mRNA-seq and m6A-seq datasets (Genes with increased m6A modification after silencing ALKBH5) (GSE87515). (e) RT-qPCR analysis of HUH-7 cells with or without silencing ALKBH5. (f) RIP-qPCR analysis of HUH-7 with or without silencing ALKBH5 in order to detect the combination of ALKBH5 with three genes (MAP3K8, MROH1, and UAP1L1). (g) M6a-IP-qPCR analysis of HUH-7 with or without silencing ALKBH5. (h) RT-qPCR analysis of Sk-hep1 with or without silencing ALKBH5. (i) Western blot analysis of the effect of cycloleucine on MAP3K8 expression. (j) Western blot analysis of the effect of mut-ALKBH5 H204A on MAP3K8 expression. (k) Western blot analysis of the effect of silencing YTHDF2 on MAP3K8 expression. (l) RT-qPCR analysis of the effect of silencing YTHDF2 on the half-life of MAP3K8 mRNA. (m) Colocalization of the YTHDF2 protein and MAP3K8 mRNA was observed by IF-FISH. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. All data are presented as the means ± SEM. Student's t-test for independent samples and unequal variances was used to assess statistical significance. Comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Comparisons at different time points were analyzed by repeated-measures ANOVA. Cell experiments were independently repeated three times.