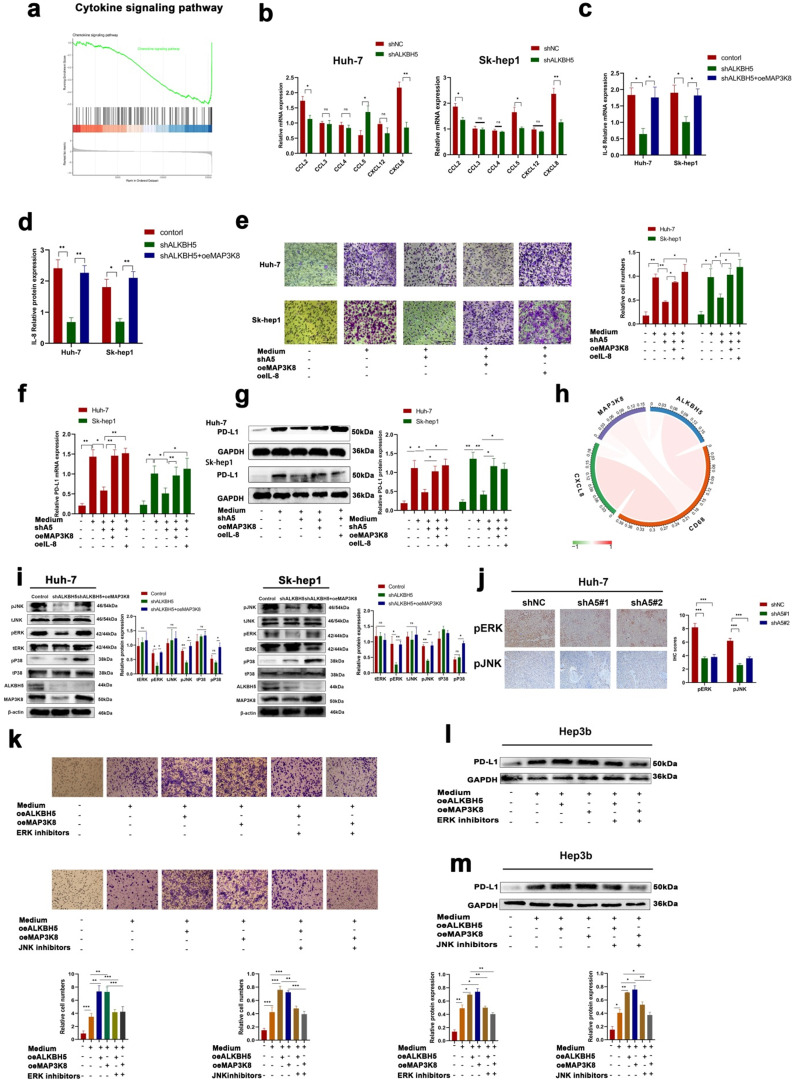
Figure 6.
MAP3K8 mediates the recruitment of PD-L1+ macrophages by ALKBH5. (a) GSEA of ALKBH5 in HCC based on the above own mRNA-seq data. (b) Effect of ALKBH5 on macrophage chemokines measured by RT-qPCR. (c) Effect of MAP3K8 on IL-8 measured by RT-qPCR. (d) Effect of MAP3K8 on IL-8 measured by ELISA. (e) The effect of MAP3K8 and IL-8 on the recruitment of macrophages was detected by Transwell assay. (f) RT-qPCR of PD-L1 expression in macrophages. (g) Western blot of PD-L1 in macrophage. (h) Correlation analysis of the ALKBH5/MAP3K8/IL-8/CD68 axis based on the ICGC database. (i) Western blot analysis of the effect of ALKBH5 and MAP3K8 on ERK/JNK/p38 pathway. (j) IHC for p-JNK and p-ERK in subcutaneous tumor. (l) Effects of ERK inhibitors (LY3214996) and JNK inhibitors (JNK-IN-8) on the ability of ALKBH5 to interfere with the recruitment of macrophages in hepatoma cells (Hep3b). (l) Effects of ERK inhibitors (LY3214996) on the ability of ALKBH5 to induce PD-L1 expression of macrophage in hepatoma cells (Hep3b). (m) Effects of JNK inhibitors (JNK-IN-8) on the ability of ALKBH5 to induce PD-L1 expression of macrophage in hepatoma cells (Hep3b). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. All data are presented as the means ± SEM. Student's t-test for independent samples and unequal variances was used to assess statistical significance. Comparisons among multiple groups were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Cell experiments were independently repeated three times.