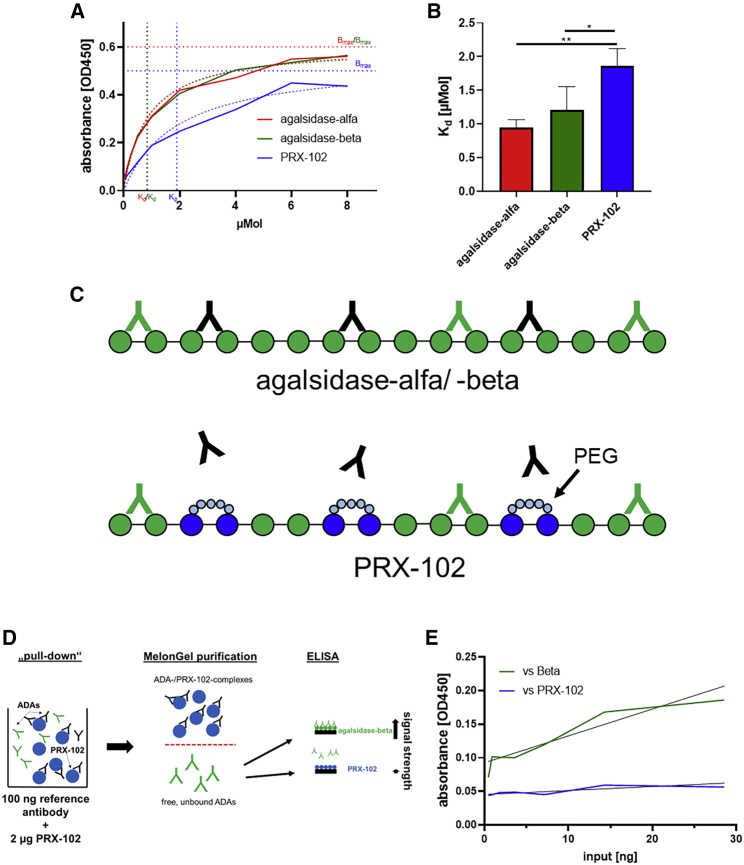
Figure 1.
Molecular characterization of a polyclonal human anti-AGAL antibody against 3 different recombinant α-galactosidase A compounds
(A and B) ELISA-based affinity measures versus agalsidase-alfa, agalsidase-beta, and pegunigalsidase-alfa (PRX-102). (C) Schematic overview of putative epitopes on the three AGALs (shown as monomers) and the potential impact of PEGylation on ADA binding. The PEGylation might form a shell around epitopes, resulting in a physical barrier. ADAs recognizing all three AGALs are highlighted in green. ADAs blocked by PEGylation are highlighted in black. (D) Workflow of the pull-down experiment and cross-over ELISA to detect the presence of agalsidase-beta-specific ADAs. (E) Pull-down experiment versus agalsidase-beta (Beta) and PRX-102. ADA, anti-drug antibodies. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.