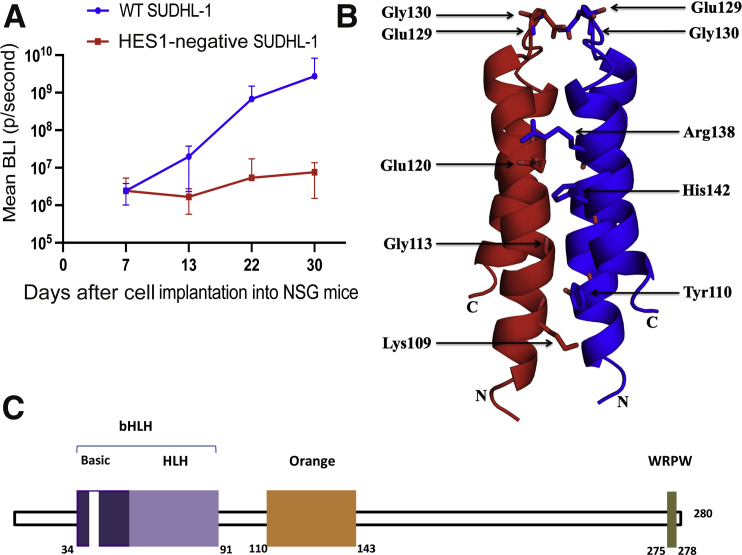
Figure 2.
Hairy and enhancer of split homolog-1 (HES1) function and structure. A: Inhibition of HES1 suppresses growth of anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive (ALK+) T-cell lymphoma (TCL) cells in vivo. HES1 gene expression was down-regulated in ALK+ TCL cells SUDHL-1 via CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system, and the cells were injected into NSG mice via tail vain. ALK+ TCL cells transfected with empty plasmid were used as a control. ALK+ TCL tumor growth curves were evaluated by bioluminescence imaging (BLI), measured at the depicted days after cell injection, with P values of <0.43 (day 7), <0.02 (day 13), <0.0002 (day 22), and <0.0002 (day 30). The depicted results are representative of two independent experiments. B: Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of HES1 Orange domain. The structure of the HES1 Orange domain, which exists as a homodimer. The interacting residues in the dimer interface are shown. Eight of the residues, based on the structure, were selected for mutation to break the dimer. C: Schematic structure of HES1 protein. HES1 has a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain, an Orange domain, and the proline-rich C-terminus with the WRPW domain. WT, wild type.