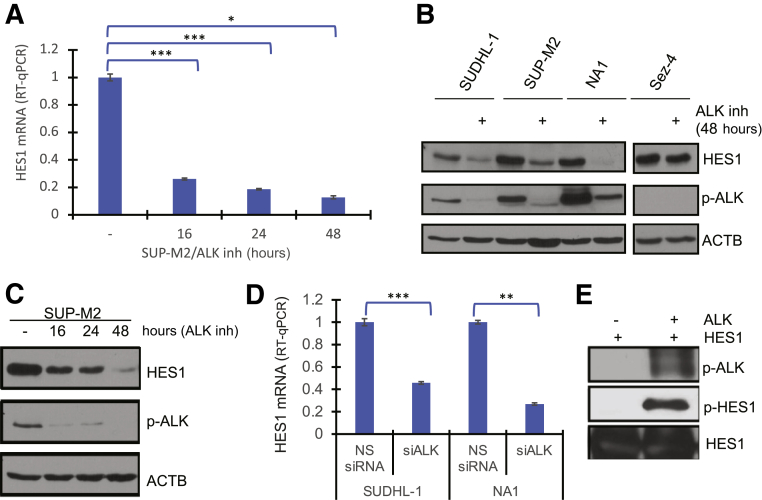
Figure 3.
Nucleophosmin–anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) dependence of hairy and enhancer of split homolog-1 (HES1) expression. A: Loss of HES1 mRNA expression detected by quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR) at 16, 24, and 48 hours in the depicted ALK+ T-cell lymphoma (TCL) cell lines exposed to 100 nmol/L of ALK inhibitor (inh) CEP-28122 or its vehicle alone. B: Western blot analysis–detected expression of HES1 and control proteins in ALK+ TCL and control ALK-negative Sez-4 cells cultured with the ALK inhibitor or its vehicle. C: Kinetics of HES1 protein loss induced by the ALK inhibitor. D: Inhibition of HES1 mRNA expression induced by ALK-specific siRNA (siALK) with non-specific (scrambled) siRNA (NS siRNA) serving as a negative control. E: ALK-mediated phosphorylation of HES1 detected using anti–phosphorylated tyrosine antibody. Detection of activated ALK [phosphorylated ALK (p-ALK)] using antibody against autophosphorylation site of ALK (Tyr 1604) served as a positive control. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. ACTB, β-actin; p-HES1, phosphorylated HES1.