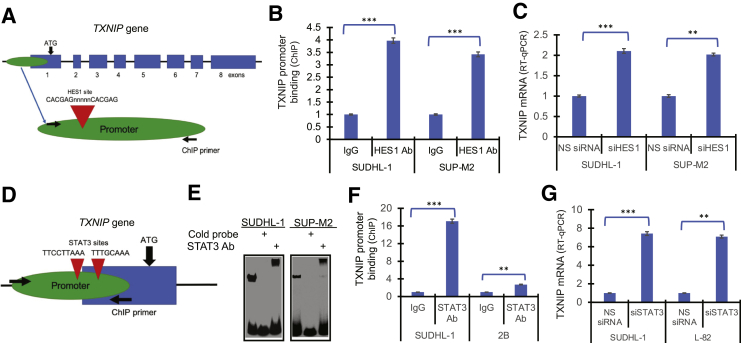
Figure 5.
Hairy and enhancer of split homolog-1 (HES1) and STAT3 inhibit thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) expression. A: Schematic diagram of TXNIP gene with depicted HES1 binding site in the gene's promoter. ATG marks transcription initiation site. Arrows indicate binding sites of primers used in chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. B: Binding of HES1 in anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive (ALK+) T-cell lymphoma (TCL) cells to the proximal HES1 promoter detected by ChIP assay. C: Induction of TXNIP mRNA expression in ALK+ TCL cells caused by siRNA-mediated HES1 depletion with cells exposed to non-specific siRNA (NS siRNA) serving as controls. D: Schematic diagram of TXNIP gene promoter region with depicted STAT3 binding sites. ATG marks transcription initiation site. Arrows indicate binding sites of primers used in ChIP assay. E: Binding of the transcription factor STAT3 to the TXNIP gene promoter in ALK+ TCL cells detected by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). Cell lysate pre-incubation with either unlabeled (cold) DNA oligonucleotide probe or STAT3-specific antibody (supershift EMSA) served as STAT3 binding specificity control. F: Binding of STAT3 to TXNIP promoter detected by ChIP assay. G: Induction of TXNIP mRNA expression triggered by STAT3 siRNA (siSTAT3) with NS siRNA serving as control. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Ab, antibody; RT-qPCR, quantitative RT-PCR; siHES1, HES1 siRNA.