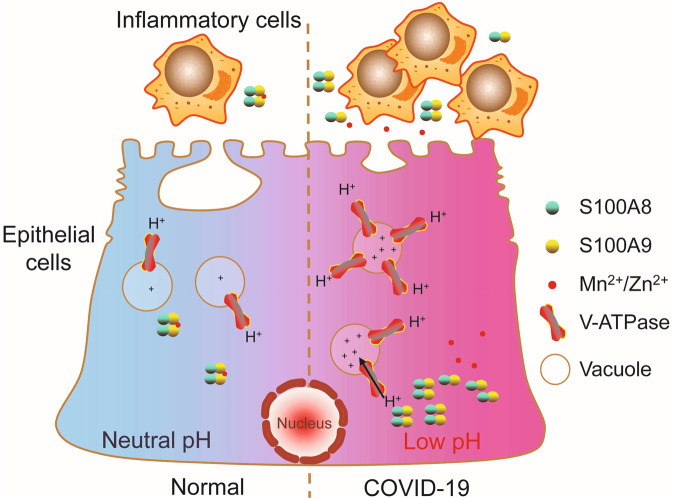
Fig. 6. The schematic diagram of intracellular pH dysregulation during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
SARS-CoV-2 increased the expression level of V-ATPase and calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) in respiratory epithelial cells. The increased V-ATPase provided an acidic microenvironment easier for the cleavage of S protein, whereas the sequester ability of calprotectin with metal ions (Mn2+/Zn2+) was reduced in acidic pH, triggering the consequent inflammation response of respiratory epithelium.