Figure 4.
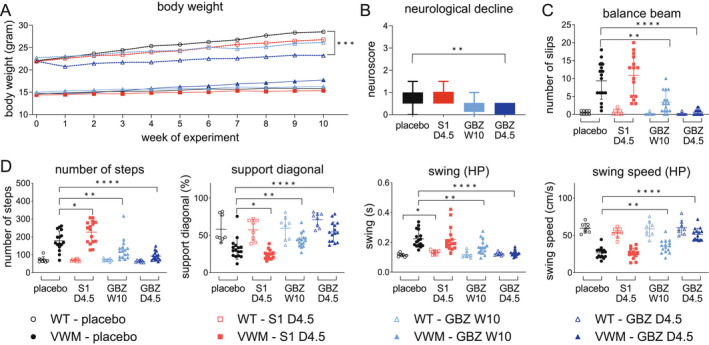
GBZ ameliorates clinical signs in 2b4 he 2b5 ho mice. Eight WT (open symbols) and 16 2b4 he 2b5 ho (VWM) mice (closed symbols) were injected daily with placebo (2.25% PEG300), 4.5 mg/kg S1 (S1 D4.5), 4.5 mg/kg GBZ (GBZ D4.5) or weekly with 10 mg/kg GBZ (GBZ W10) from an age of 6–8 weeks onwards. Injections were placed alternating on left‐ or right‐hand side of the abdominal midline. One mouse displayed signs of epilepsy 2 days after daily injections with 4.5 mg/kg GBZ, was found dead the day after and was omitted from the study. Autopsy did not show signs of infection or other causes for early demise. Graphs show mean phenotypic measures: (A) body weight; (B) neuroscores in VWM mice indicating neurological deterioration; (C) number of slips on balance beam (one S1‐treated VWM mouse was unable to traverse the balance beam and was excluded from analysis); D‐G, gait parameters on the CatWalk in different categories (HP, hind paws): (D) run characterization; E, interlimb coordination; F, temporal; G, kinetic. Neuroscores are 0 in all WT mice (not plotted). Treatment effects by GBZ and S1 were analyzed only for parameters that statistically differed between placebo‐treated WT and placebo‐treated VWM mice. Statistical analyses investigating compound‐related differences in body weight were performed with a repeated measures two‐way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett's correction. Balance beam performance was examined with a Welch's ANOVA and a Dunnett's correction and neuroscore with a Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's correction. CatWalk data was analyzed with a Kruskal–Wallis with Mann–Whitney U correction. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
