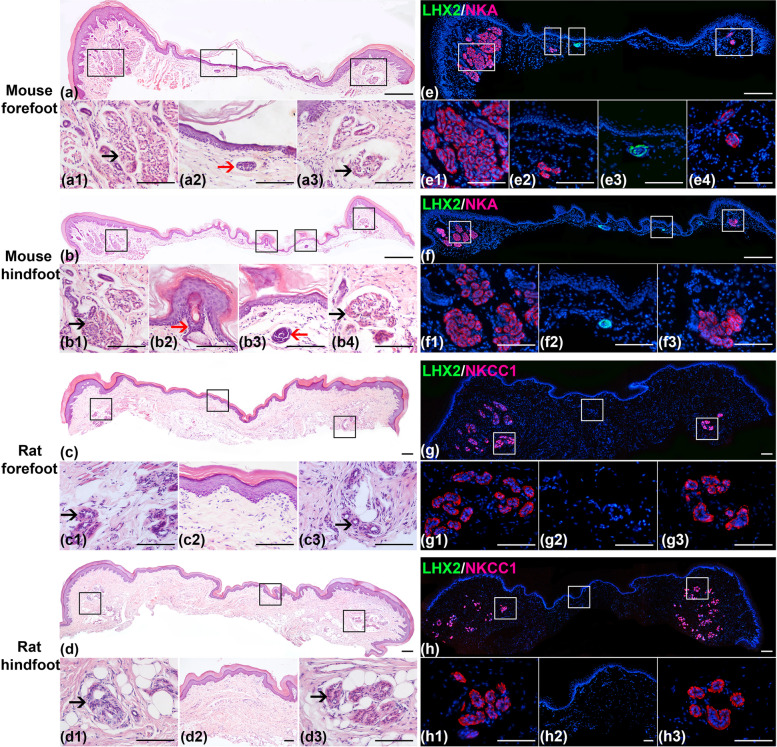
Fig. 2.
Histological staining of the volar skin of C57BL/6 mice and SD rats. The slightly raised structures on both sides of the tissue sections are the footpads and the relatively flat structures in the middle of the tissue sections are IFPs. a–d HE staining of the volar skin in mouse forefoot (a), mouse hindfoot (b), rat forefoot (c), and rat hindfoot (d). (a1, a3, b1, b4, c1, c3, d1, d3) and (a2, b2, b3, c2, d2) are magnified views of the footpads and IFPs in the boxed area shown in (a–d), respectively. Red arrows indicate HFs, and black arrows indicate ESGs. e–h Double immunofluorescent staining of LHX2/NKA or LHX2/NKCC1 of the volar skin in mouse forefoot (e), mouse hindfoot (f), rat forefoot (g), and rat hindfoot (h). LHX2, HF marker (green). NKA and NKCC1, ESG markers (red). The cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (e1, e4, f1, f3, g1, g3, h1, h3) and (e2, e3, f2, g2, h2) are magnified views of the footpads and IFPs in the boxed area shown in (e–h), respectively. 5 mice and 5 rats were used. The number of mouse forefoot, mouse hindfoot, rat forefoot and rat hindfoot were 10, respectively. Scale bar, 100 μm (a, b, c, e, f, g, h lower panels), 300 μm (a, b, e, f, g, h upper panels). Abbreviations: NKA, sodium potassium ATPase α1; NKCC1, Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter 1; LHX2, LIM Homeobox 2