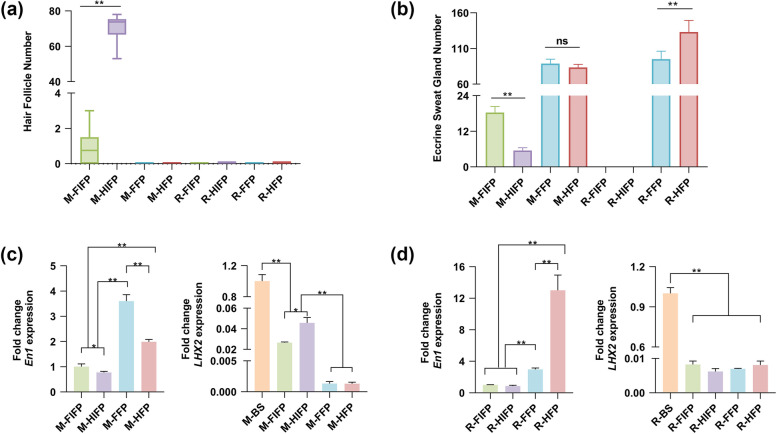
Fig. 3.
The number and gene expression of ESGs and HFs. a Quantification of HFs in the footpads and IFPs of mouse forefoot (n = 60), mouse hindfoot (n = 20), rat forefoot (n = 20), and rat hindfoot (n = 20). 30 mice and 10 rats were used. The median and inter-quartile ranges are plotted. b Quantification of ESGs in the footpads and IFPs of mouse forefoot (n = 20), mouse hindfoot (n = 20), rat forefoot (n = 20), and rat hindfoot (n = 20). 10 mice and 10 rats were used. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation. a–b Every value represents average number of ESGs and HFs in the footpads or IFPs of a single animal’s two forefeet or two hindfeet. c–d qRT-qPCR: differential expression of En1 in four tissues of mouse or rat (FIFP, HIFP, FFP, HFP). Differential expression of LHX2 in five tissues of mouse or rat (BS, back skin, as a positive control; FIFP, HIFP, FFP, HFP). For all qRT-PCR analyses, gene expression was normalized to the reference gene (GAPDH). Values are reported as mean ± standard deviation. a-d Kruskal-Wallis (a), Welch’s ANOVA (b), one-way ANOVA tests (c, d) were used to test for differences among multiple groups of the data. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. “ns” means no statistical significance. Abbreviations: BS, back skin; FIFP, fore inter-footpad; HIFP, hind inter-footpad; FFP, fore-footpad; HFP, hind-footpad; M, mouse; R, rat