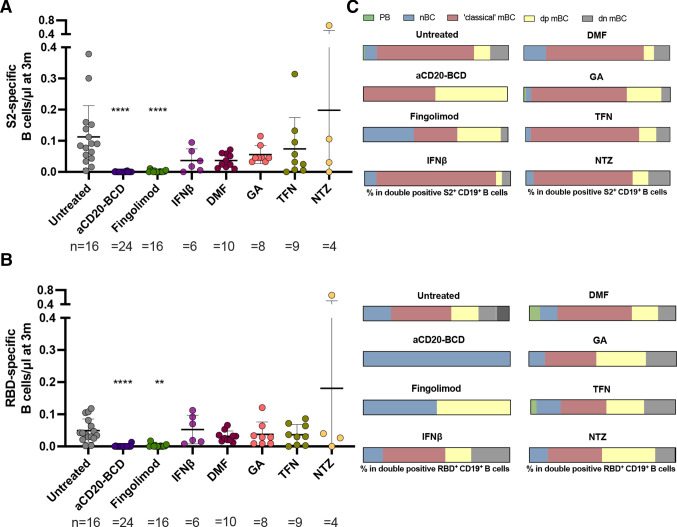
Figure 3.
Decreased and naïve B cell-shifted RBD-specific and S2-specific B cell responses in aCD20-BCD-treated and fingolimod-treated patients with MS. (A, B) Absolute numbers of RBD-specific (A) and S2-specific (B) CD19+ B cells at 3 months post primary vaccination for each treatment group. Mean and SD are indicated. Each dot represents the determined value for a patient. The number of patients for each respective group is provided below each plot. Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test were performed to test treatment groups in comparison to untreated patients. Significance levels indicate differences between treatment groups and the untreated cohort and are reported as: **p≤0.01, ****p≤0.0001. Non-significant results were not reported. (C) Frequencies of CD19+CD20low/-CD27++CD38++ plasma blasts (PB), CD19+CD20+CD27- IgD+ naïve B cells (nBC), CD19+CD20+CD27+ IgD- memory B cells (mBC), CD19+CD20+CD27+ IgD+ MBC (dp MBC) and CD19+CD20+CD27- IgD- B cells (dn MBC) in RBD-specific and S2-specific CD19+ B cells per treatment group. B cell gating is shown in online supplemental figure 4. RBD, receptor binding domain. DMF, dimethyl fumarate; GA, glatiramer acetate; IFNβ, interferon-β; m, month/s; MS, multiple sclerosis; TFN, teriflunomide; NTZ, natalizumab.