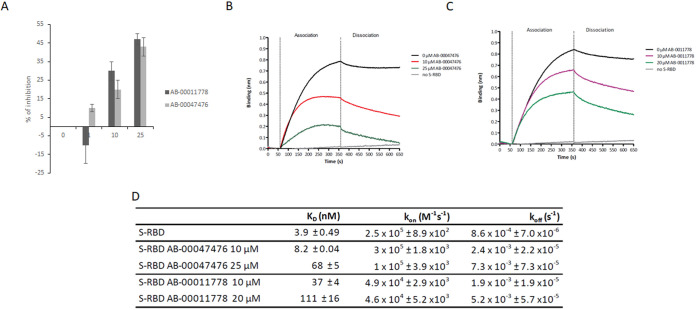
FIG 4.
Effects of AB-00011778 and AB-00047476 on the in vitro S-RBD/ACE2 interaction using AlphaLISA and biolayer interferometry (BLI) technologies. (A) SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD(His)6 and human ACE2-Biot interactions were first monitored by AlphaLISA using a 3 nM concentration of each protein. Increasing concentrations of AB-00011778 and AB-00047476 were incubated for 30 min with S-RBD(His)6 before being mixed with ACE2-Biot for 2 h. The microplate results were read after 2 h of incubation with the anti-6×His acceptor and streptavidin donor beads. Data obtained with the compounds were compared to the DMSO control and are reported as the mean percentage of binding inhibition from two or three independent experiments in duplicate ± standard deviation. (B and C) The effect of the molecules on the binding kinetics of S-RBD to biotinylated ACE2 immobilized on a streptavidin biosensor was also determined using BLI experiments. Baseline reaction buffer was measured for 60 s. For the association step (300 s), each loaded biosensor was dipped into 50 nM S-RBD(His)6 preincubated for 15 min with increasing concentrations of AB-00011778 or AB-00047476. The dissociation step was subsequently measured for 300 s. Sensorgram curves shown in panels B and C were plotted using Prism 5.0 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA). The association and dissociation experimental curves were locally fitted using a 1:1 binding model with BLItz Pro 1.1 software. (D) Kinetic binding parameters (kon, koff) and the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) were determined as the means of results of two to three independent experiments. Data are shown as the means of results of two to three independent experiments ± standard deviations.