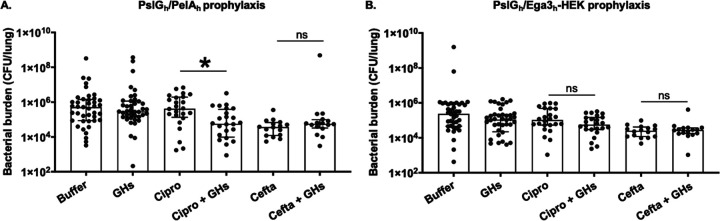
FIG 4.
Specific GH-antibiotic combinations reduce bacterial burden in an acute mouse model of pulmonary P. aeruginosa infection. Mice were intratracheally infected with 3 × 107 P. aeruginosa CFU coadministered with or without PslGh-PelAh (A) or PslGh-Ega3h-HEK (B) and then treated as indicated with 10 mg/kg ciprofloxacin or 25 mg/kg ceftazidime every 8 h for 1 day. Pulmonary bacterial burden was determined by CFU quantification. Bars represent the medians with interquartile ranges of at least 2 independent experiments with ≥16 mice per group. *, significant difference (P = 0.0347) between combinations of GHs and ciprofloxacin and ciprofloxacin alone; ns, no significant difference (P > 0.9999), as determined by the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison test. Cipro, ciprofloxacin; Cefta, ceftazidime.