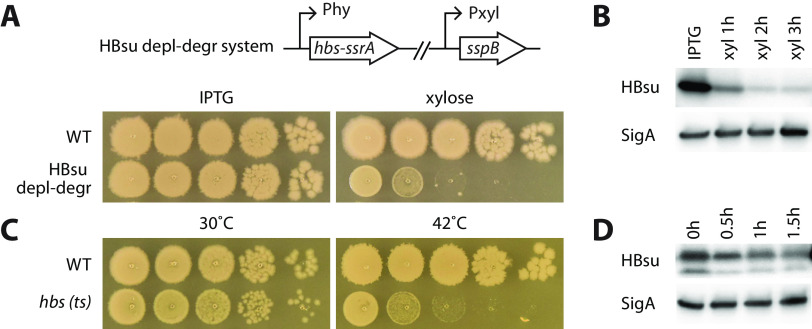
FIG 1.
HBsu is required for the growth of Bacillus subtilis. (A) An HBsu depletion-degradation (depl-degr) system was constructed. The gene fusion hbs-ssrA was expressed from an IPTG-inducible promoter (Phy) at the endogenous locus of hbs. E. coli sspB adaptor protein was expressed from a xylose-inducible promoter (Pxyl). The HBsu depletion-degradation strain (BWX1336) was grown in liquid medium containing 0.5 mM IPTG. Cultures were washed three times using medium without the inducer and then normalized to an OD600 of 2. The cultures were serially diluted and spotted on agar plates containing 0.5 mM IPTG (HBsu+) or 0.5% xylose (depletion-degradation). Wild-type B. subtilis (PY79) was used as a control. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 12 h. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the HBsu depletion-degradation system. The HBsu depletion-degradation strain (BWX1336) was grown in CH medium in the presence of 0.5 mM IPTG. Cells were washed three times using CH medium and then resuspended into CH medium containing 0.5% xylose (xyl). Samples were taken 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after resuspension. When OD600 reached 0.5, the culture was diluted 1:5 in warm CH containing 0.5% xylose to maintain exponential growth. The same growth medium and condition was used for microscopy and whole-genome sequencing experiments throughout the study. Samples were blotted using HBsu polyclonal antibodies. SigA controls for loading. (C) Serial dilutions of WT and hbs(ts) (BWX4331) strains grown at 30°C and 42°C. The two strains were grown at 30°C, normalized to an OD of 2, serially diluted, and spotted on LB plates, which were incubated at indicated temperatures for 14 h. (D) Immunoblot analysis of hbs(ts) (BWX4331) strain. Cells were grown in CH medium at 30°C and shifted to 42°C for indicated times. When OD600 reached 0.5, the culture was diluted 1:5 in warm CH to maintain exponential growth. The same growth condition was used for microscopy and whole-genome sequencing experiments in this study. The membranes were blotted using HBsu polyclonal antibodies. SigA controls for loading.