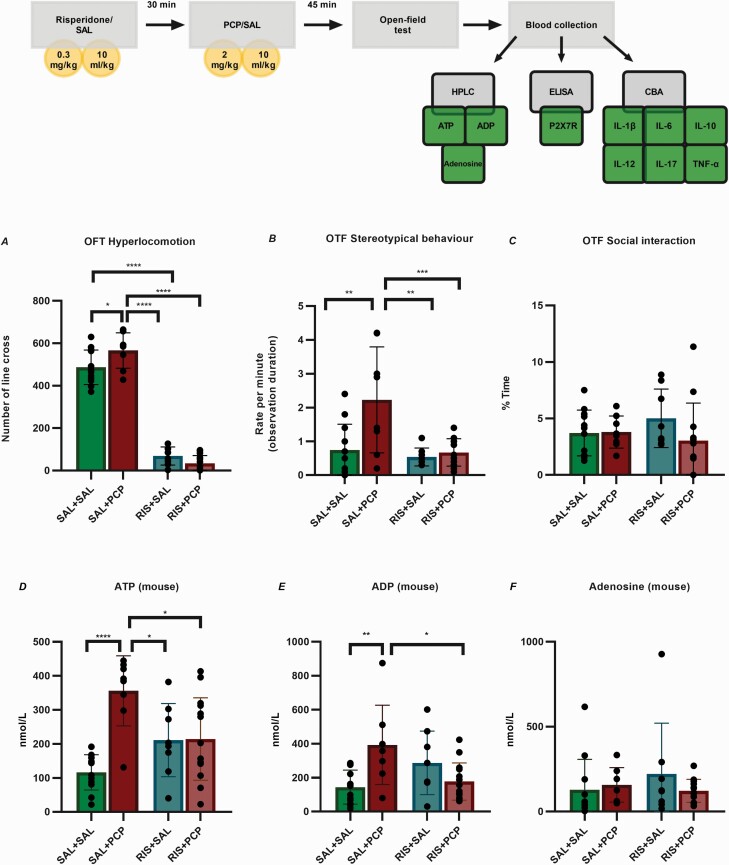
Figure 4.
Study design, behavioral validation of the phencyclidine (PCP)-induced acute mouse model of schizophrenia, and purine levels in mouse plasma. (A-B) PCP treatment significantly increased the basal locomotor activity and stereotypical behaviors, whereas risperidone (RIS) pretreatment significantly decreased both phenomena. (C) Neither PCP nor RIS treatment affected social interactions. (D) The level of ATP in the saline (SAL)+PCP group was significantly higher than those in all the other treatment groups. The ATP levels in PCP-treated mice were significantly lower than those in mice receiving RIS. (E) The levels of ADP in the SAL+PCP group were significantly increased compared with those in the SAL+SAL and RIS+PCP groups. (F) The levels of Ado did not significantly differ between the groups. RIS alone did not affect the extracellular purine levels. SAL+SAL N = 12; SAL+PCP, n = 8; RIS+SAL N = 8; RIS+PCP, n = 14. The data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. P values and statistical details are provided in supplementary Table 2. Abbreviations: Ado, adenosine; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ANOVA, analysis of variance; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CBA, cytometric bead array; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; IL, interleukin; OFT, open-field test.