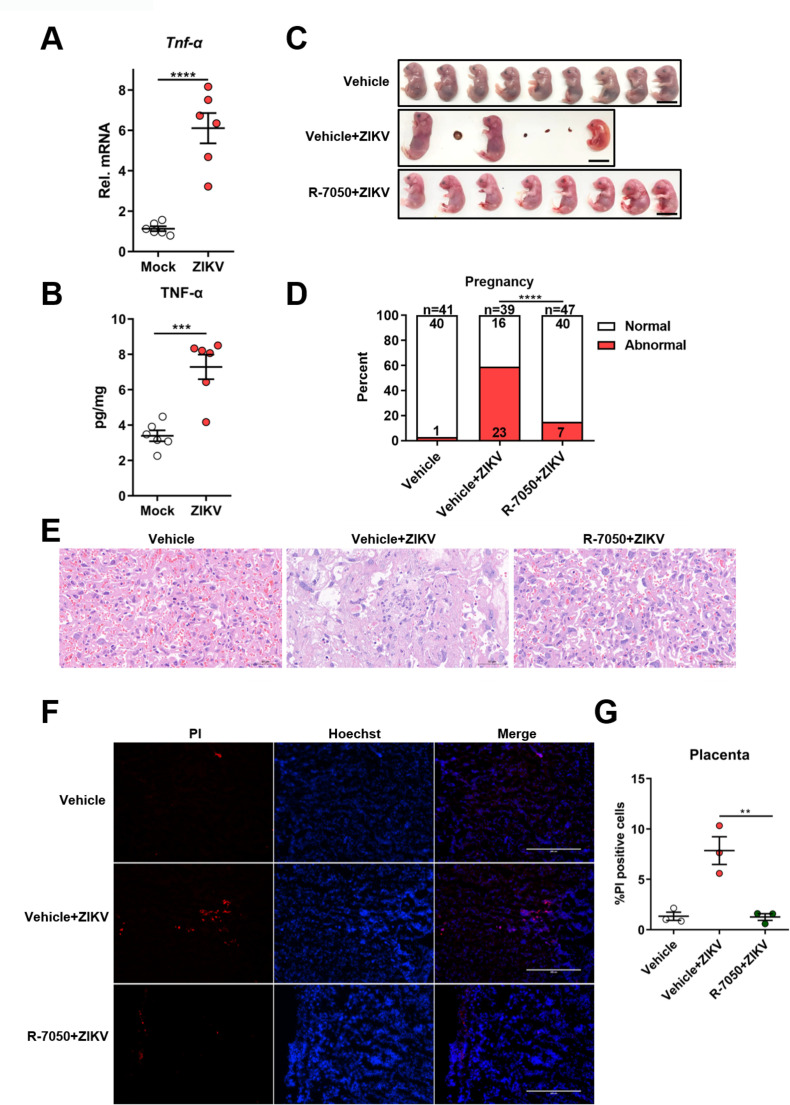
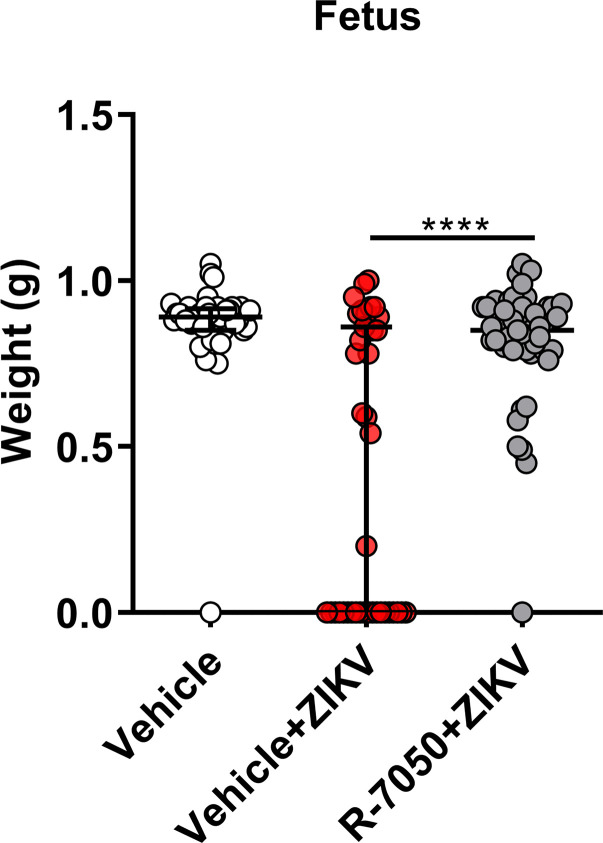
Figure 6. Induction of TNF-α expression contributes to placental damage in Zika virus (ZIKV)-infected pregnant mice.
(A–B) The pregnant C57BL/6N mice were mock-infected or intravenously infected with 1×106 PFU of ZIKV H/PF/2013 strain at embryonic day 9.5 (E9.5). At E16.5, placentas were collected and the mRNA level and concentration of TNF-α in mouse placentas were determined by RT-qPCR (A) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (B), respectively (n=6). (C–G) The pregnant C57BL/6N mice were intravenously infected with 1×106 PFU of ZIKV H/PF/2013 strain at E9.5, followed by treatment with R-7050 (7 mg/kg, i.p.) or DMSO every other day. At E16.5, mice were sacrificed and the placentas and individual fetuses were collected. Representative images of fetuses from mock- and ZIKV-infected dams treated with R-7050 or vehicle at E16.5 are shown. Scale bar, 1 cm (C). The percentages of fetuses that were affected (i.e., had undergone resorption, or exhibited any sign of growth restriction, or malformation) were calculated. Numbers on bars indicate normal fetuses (top) or affected fetuses (bottom) (D). Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed to show the pathological features of placentas at E16.5. The asterisks indicate abnormal spheroid structure. Arrows indicate necrotic trophoblast cells. Arrowheads indicate thrombi. Scale bar, 50 μm (E). Propidium iodide (PI) was intravenously injected into the mice before scarification. Representative placenta section images are shown (F) and PI-positive cells were quantified (n=3) (G). Scale bar, 400 μm. For (A), (B), and (G) significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. For (D), significance was determined by Fisher’s exact test. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001.