Figure 2.
Validation of the RET::GRB2 fusion protein in the pheochromocytoma and in vitro
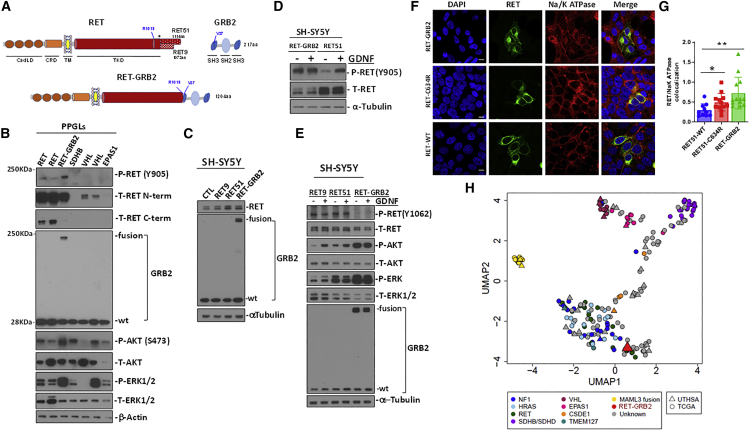
(A) Diagram of wild-type (WT) RET, displaying relevant domains as indicated (CadLD, cadherin-like domains; CRD, cysteine-rich domain; TM, transmembrane domain; TKD, tyrosine kinase domain). The two main RET isoforms diverge at amino acid (aa) 1,063 (∗) with either 51 (RET51) or 9 (RET9) distinctive aa at the C terminus; WT GRB2 contains two SH3 domains flanking one SH2 domain. The RET (R1013) and GRB2 (V27) breakpoint sites are indicated; full-length RET::GRB2 fusion spans 1,204 aa.
(B) Western blot of protein lysates from PPGLs carrying mutations in RET, SDHB, VHL, and EPAS1 genes, and the RET::GRB2 fusion, probed with phosphorylated (P) RET (Y905) and two distinct total (T) RET antibodies directed at the extracellular, N-terminal (N-term) region around D320 and C-terminal (C-term) region beyond aa 1,100. GRB2 shows both the WT and fusion product, P- and T- AKT; ERK1/2, β-actin is a loading control; two technical replicates were performed.
(C) SH-SY5Y cells stably expressing RET9, RET51, RET::GRB2, and a control vector, probed with RET, GRB2, and α-tubulin as a loading control; three biological replicates were performed.
(D) SH-SY5Y cells expressing RET::GRB2 or RET51 were starved of serum for 3 h and exposed to 100 ng/mL GDNF (+) or vehicle (−) for 10 min, and lysates were probed with P-RET Y905 or T-RET; α-tubulin is a loading control; experiments were repeated three times.
(E) SH-SY5Y cells expressing RET::GRB2, RET 9, or RET51 constructs were treated with GDNF as in (D). Lysates were probed with GRB2 and T- and P- AKT, ERK1/2, T RET, and RET phosphorylated at Y1062, a region excluded from the RET::GRB2 fusion; α-tubulin is a loading control; experiments were repeated three times.
(F) Confocal microscopy of HEK293T cells expressing WT, mutant (C634R) RET, or RET::GRB2 fusion, labeled with a tag antibody in green (MYC for WT and C634R RET or hemagglutinin [HA] for RET::GRB2 fusion) and a membrane marker, Na/K ATPase (red). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). A merged image is shown in the right panels. Scale bar: 10 μm.
(G) Quantification of the colocalized signals between RET and the Na/K ATPase using ImageJ from multiple independent images (n = 10–13 cells/genotype, two biological replicates). One way ANOVA, p = 0.048; ∗p = 0.02, two-tailed t test; ∗∗p = 0.0042, two-tailed t test.
(H) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plot of RNA-seq data from pheochromocytomas/PPGLs of our cohort (n = 30, UTHSA) and TCGA (n = 178), color-coded by genotype; gray symbols are tumors with unknown mutations; RET::GRB2 fusion (red triangle).