Fig. 3.
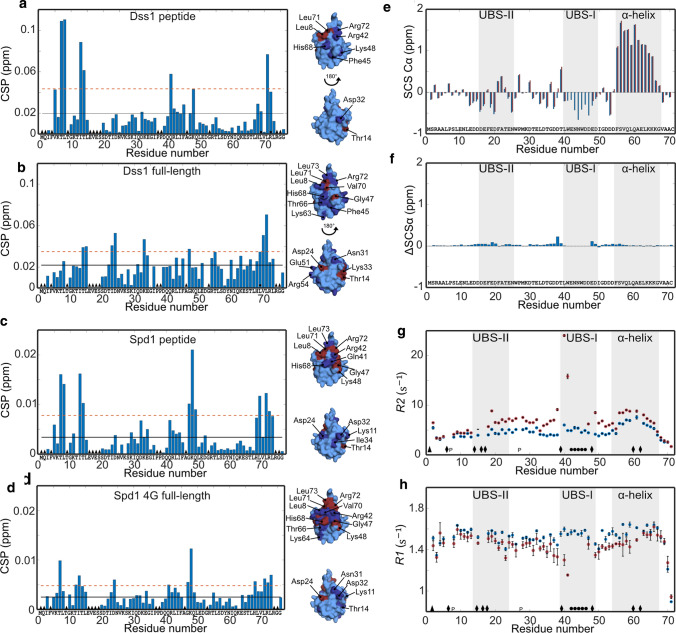
The context of the DisUBM affects binding. a CSP per residue of 100 µM 15N-labeled ubiquitin added 3000 µM Dss1 peptide. The black line indicates the average CSP and the dashed red line the average CSP + one standard deviation. Black triangles indicate unassigned residues, and black circles line broadening upon addition of Dss1. Surface representations of ubiquitin with affected residues in dark blue (above average CSP) and red (above average + one standard deviation) highlighted are shown to the right. b Same as a but with 440 µM full-length Dss1. c Same as a but with 1000 µM Spd1 peptide. d Same as a but with 290 µM 4G Spd1. e SCS of the Cα atoms of 1 mM 13C-15 N-labeled Dss1 alone (blue) or with 2 mM ubiquitin (red). Gray bars indicate the transient helix and ubiquitin-binding sites in Dss1 as identified by Paraskevopoulos et al. [36]. f Differences between the SCSs shown in e of Dss1 with and without ubiquitin. g R2 and h R1 values of 500 µM 15 N-labeled Dss1 without (blue) and with (red) 1 mM ubiquitin. The error bars are standard deviations from triplicate recordings on the same sample. Triangles are unassigned residues, diamonds residues with peak overlap, “p” indicates prolines and circles peaks that disappear upon addition of ubiquitin