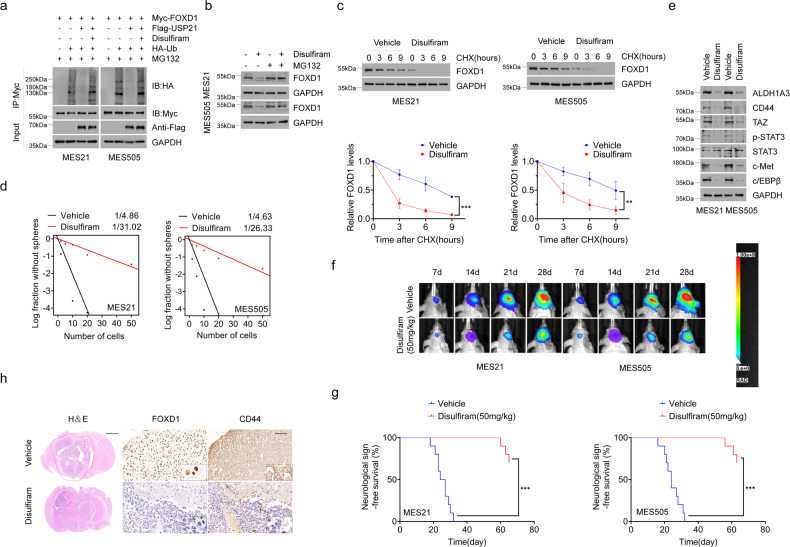
Fig. 5. Pharmacological inhibition of USP21 by disulfiram promotes FOXD1 ubiquitination and retards tumor growth.
a Co-IP showing that the ability of USP21 to remove ubiquitin moieties from polyubiquitinated FOXD1 was almost completely abrogated by disulfiram. b Western blotting showing that disulfiram, like USP21 knockdown, promotes FOXD1 ubiquitination and degradation. c Western blotting showing that disulfiram induced a marked decrease in the stabilization of FOXD1 protein. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01. d In vitro limiting dilution sphere-forming frequency showing that the disulfiram treatment reduced the tumorsphere formation frequency of MES21 and 505 GSCs. **P < 0.01. e Western blotting showing that disulfiram treatment notably inhibited the core MES GSC markers including ALDH1A3, CD44, TAZ, p-STAT3, c-MET and c/EBPβ. f Representative bioluminescent images showing that tumor-bearing mice receiving disulfiram treatment showed retarded tumor growth compared with vehicle-treated mice. n = 10. g Kaplan–Meier survival curves showing that mice bearing xenograft tumors receiving disulfiram treatment had a shorter lifespan than vehicle-treated mice. n = 10, ***P < 0.001, Log-rank test. h Representative H&E and IHC images showing that disulfiram attenuated the tumor growth and the expression of FOXD1 and CD44 in tumor tissues.