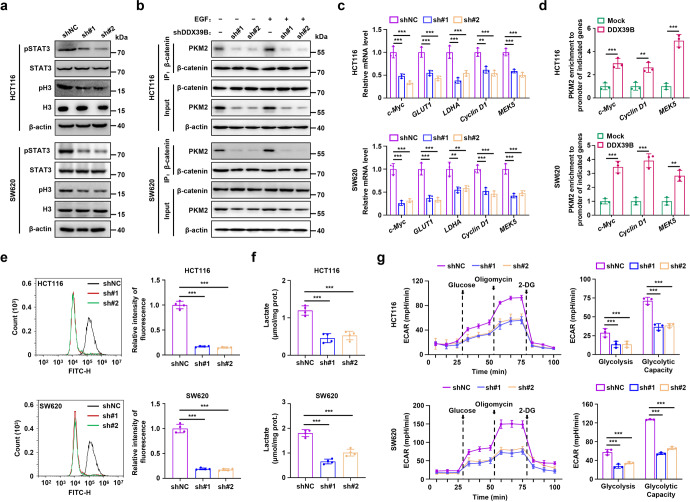
Fig. 6.
DDX39B enhances nuclear PKM2 function and aerobic glycolysis in CRC cells. a Phosphorylation of STAT3Y705 and histone H3T11 in DDX39B-knockdown CRC cells was detected by western blotting. b DDX39B-deficient CRC cells were treated with or without 150 ng/ml EGF, and the association of PKM2 with β-catenin was detected by immunoprecipitation assay. c The relative mRNA levels of c-Myc, GLUT1, LDHA, Cyclin D1, and MEK5 were measured by qPCR in CRC cells stably expressing shNC or shDDX39B. d Binding of PKM2 to the promoters of c-Myc, Cyclin D1, and MEK5 was detected by chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. e Glucose uptake in DDX39B-knockdown CRC cells was detected by flow cytometry using the fluorescent glucose analog 2-NBDG. f The lactate levels in DDX39B-deficient CRC cells were quantified. g The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) of DDX39B-knockdown CRC cells was monitored, and the levels of glycolysis and glycolytic capacity were calculated. Data are presented as mean ± SD. The p values were determined by Student’s t test (d) or one-way ANOVA (others). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001