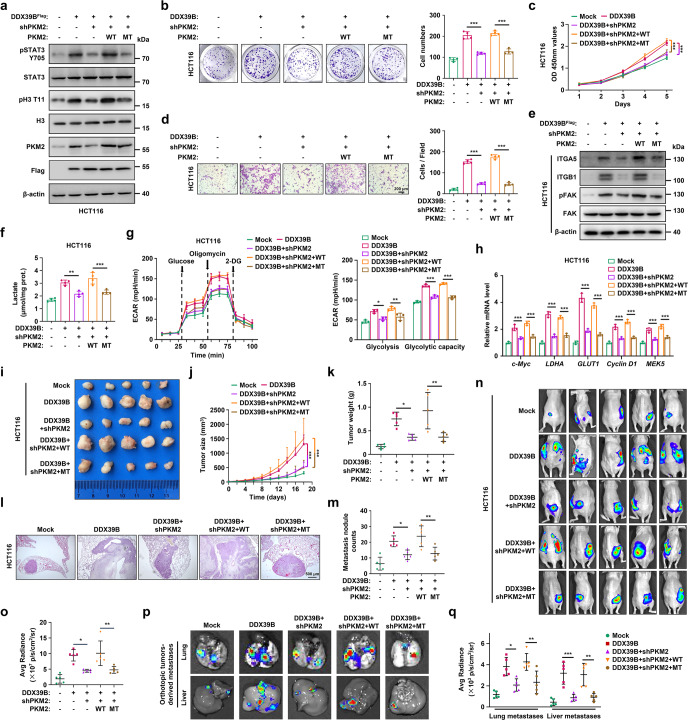
Fig. 8.
Blocking PKM2 nuclear accumulation impairs DDX39B-triggered Warburg effect and tumorigenicity in CRC. a–q HCT116 cells simultaneously expressing DDX39B cDNA and PKM2-shRNA were re-introduced into RNAi-resistant PKM2WT or PKM2R399/400A mutant (MT), respectively. a Phosphorylation of STAT3Y705 and histone H3T11 was detected by western blotting. b The cell proliferation was measured by colony formation assay. c Cell viability was measured by CCK8 assay. d Cell motility was determined by transwell migration assays. e The indicated protein levels were detected by western blotting. f The lactate production in indicated HCT116 cells was quantified. g The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) of indicated HCT116 cells was monitored, and the levels of glycolysis and glycolytic capacity were calculated. h The relative transcriptions of c-Myc, GLUT1, LDHA, Cyclin D1 and MEK5 were measured by qPCR. The growth and metastatic abilities of indicated HCT116 cells in vivo were assessed in nude mice by subcutaneous and lung metastasis tumor models (n = 5), respectively. The images (i), tumor sizes (j), and tumor weights (k) of subcutaneous xenografts are presented. Representative pulmonary metastases detected by H&E staining are shown (l), along with the number of metastatic nodules (m). n–q Indicated HCT116 cells were orthotopically inoculated into the cecum of mice (n = 5). At day 60 after inoculation, the bioluminescent images of orthotopic tumors were captured (n) and light emissions were quantified (o). The representative bioluminescent images of the isolated lungs and livers were obtained (p), and the metastases were quantified (q). Data are presented as mean ± SD. The p values were obtained by two-way ANOVA (c, j) or one-way ANOVA (others). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001