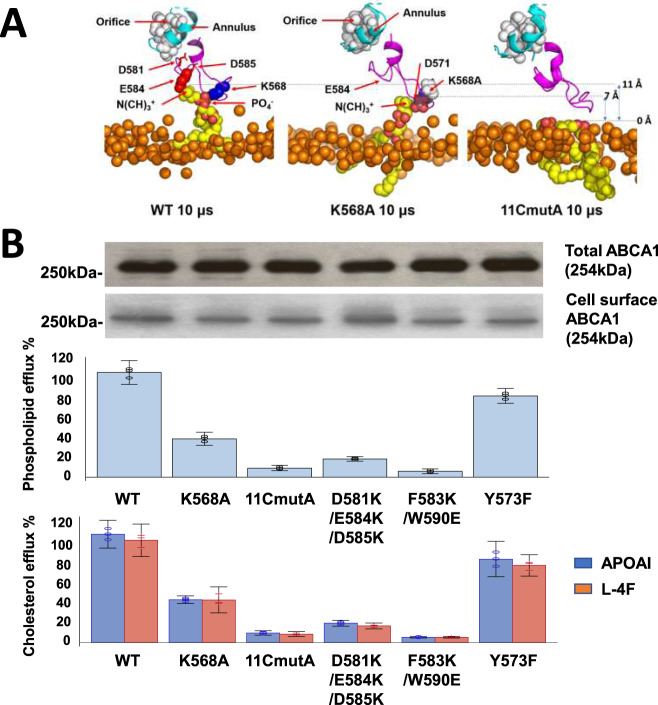
Fig. 3. Charged amino acids in the gateway promote PL extraction and lipid export by ABCA1.
A Extraction of POPC molecules from the membrane bilayer into the gateway by wild-type and mutated ABCA1. Final frames of the three 10 μsec CGMD simulations showing the gateway (magenta, cartoon), annulus (cyan, cartoon), and annulus orifice (white, space-filling) for different ABCA1 monomers inserted into a POPC bilayer. The ABCA1 monomers are wild-type (WT, left panel), K568A (middle panel), and 11CmutA (mutation of all 11 charged residues to alanine, right panel), respectively. The position of the upper monolayer surface in each image is shown by orange space-filling phosphorus atoms. The single POPC molecule extracted by the ABCA1 monomer of WT and K568A are shown in yellow (space-filling). The 11CmutA monomer failed to extract POPC (yellow, space-filling). Left panel, K568 is space-filling blue, E584 is space-filling red and D581 and D585 are stick red; middle panel, K568A is space-filling white, D571 is space-filling red. B Effects of gateway mutations K568 and 11CmutA on PL and cholesterol efflux by ABCA1. Wild-type, K568A, 11CmutA, D581K/E584K/D585K, F583K/W590E, and Y573F ABCA1 were expressed in BHK cells. PL and cholesterol efflux by the cells were quantified after incubation with APOA1 or an equal weight of L-4F, an APOA1-peptide mimetic. Lipid efflux and ABCA1 expression were quantified as described in Methods. Relative cholesterol and phospholipid efflux are normalized to WT and are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments with three replicates per experiment. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.