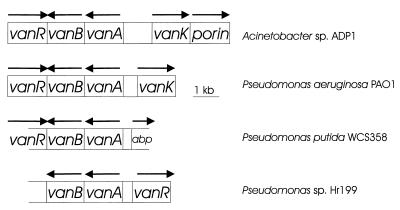
FIG. 5.
Comparative organization of the vanAB chromosomal region. From top to bottom in the figure, the percent amino acid identities to the corresponding proteins in Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1, followed in parentheses by the numbers of aligned residues, are 69% (340), 69% (346), and 72% (340) for VanA; 46% (314), 47% (316), and 48% (316) for VanB; 61% (163), 57% (26), and 43% (166) for the regulatory protein in the GntR family (VanR); and 50% (415) for VanK. The region labelled abp could encode a protein with up to 33% identity over 148 aligned residues with a protein in various bacteria thought to be the periplasmic ATP-binding component of an ATP-binding cassette-type transport system (although this region includes a stop codon the potential open reading frame). Similarly, the size of the regulatory gene shown above assumes a frameshift in all three Pseudomonas sequences, due to mutation or sequencing error (and not included in the calculation of amino acid identity for the protein in the bottom two Pseudomonas sequences). The P. aeruginosa genes are present on one contig from the 15 September 1998 release of data from the Pseudomonas Genome Project. Arrows indicate the directions of transcription.