FIGURE 2.
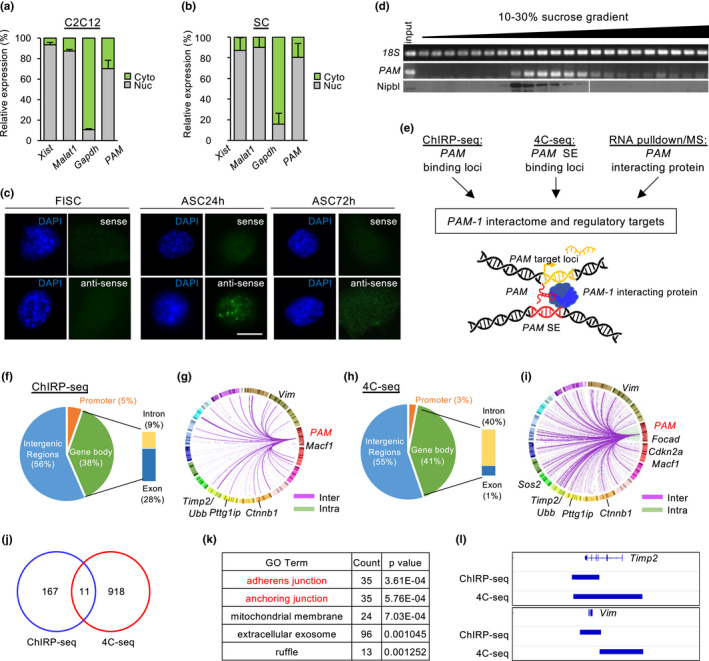
PAM is a nuclear‐retained lncRNA, forming cis and trans chromosomal interactions (a,b). Cellular fractionation of (a) C2C12 cell line and (b) ASC showed PAM was enriched in nucleus not cytosolic fraction. Xist and Malat1 were positive control for nuclear fraction, Gapdh was positive control for cytosolic fraction. (c) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in FISC, ASC24h and ASC72h using PAM antisense (AS) probe showed nuclear localization of PAM, sense probe (S) was used as negative control. Scale bar: 10 μm (d) Cellular fractionation using sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation showed PAM was co‐localized in fractions containing nuclear protein Nipbl. (e) Experimental workflow to discover PAM interactome and regulatory targets. For details and controls, see experimental procedures. (f) Pie chart showing distribution of PAM seRNA interacting chromatin across the genome in ChIRP‐seq. (g) Circos plot showing genes associated to PAM seRNA interacting chromatin, each line in the plot represents an interaction, line colors represent inter‐chromosomal (purple) or intra‐chromosomal (green) interactions. Chromosome numbers were colored and arranged in clockwise direction. Top‐ranked genes were named in the figure. (h) Pie chart showing distribution of PAM SE interacting chromatin across the genome in 4C‐seq. (i) Circos plot showing genes associated to PAM SE interacting chromatin, each line in the plot represents an interaction, line colors represent inter‐chromosomal (purple) or intra‐chromosomal (green) interactions. Chromosome numbers were colored and arranged in clockwise direction. Top‐ranked genes were named in the figure. (j) Venn diagram showing overlapping loci between ChIRP‐seq of PAM seRNA and 4C‐seq of PAM SE. (k) Table showing top‐ranked gene ontology (GO) terms of genes associated with overlapping loci from ChIRP‐seq of PAM seRNA and 4C‐seq of PAM SE. (l) Genome browser tracks showing Timp2 and Vim as examples of PAM inter‐chromosomal targets. ChIRP‐seq tracks indicate regions of broad peaks enriched with PAM seRNA binding. 4C‐seq tracks indicate fragments cut by two restriction enzymes and showing significant chromatin interaction with PAM SE
