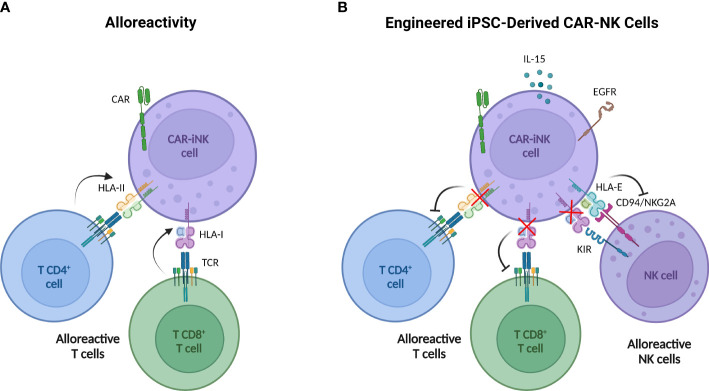
Figure 2.
Multi-engineered iPSC-derived CAR NK cells designed to overcome T cell alloreactivity. (A) iPSC-derived CAR NK cells may be rejected by host alloreactive T cells due to the recognition of non-self HLA I by CD8+ T cells and HLA II by CD4+ T cells. (B) Engineered iPSC-derived CAR NK cells incorporate six modifications through three gene-editing steps. 1) The β-2-microglobulin (β2M) disruption to avoid HLA-I expression with the simultaneous insertion of a transgene encoding HLA-E protein (tethered with β2M and a peptide) impedes NK cell killing activity by “missing-self” recognition. 2) The CIITA knock-out to deplete the HLA-II expression concurrently with knock-in of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) safety switch and the interleukin 15 (IL-15). Safety switch strategy allows the elimination of iPSC-derived CAR NK by the administration of anti-EGFR antibodies and IL-15 secretion improves cell persistence. 3) CD19 CAR knock-in. Created with BioRender.com.