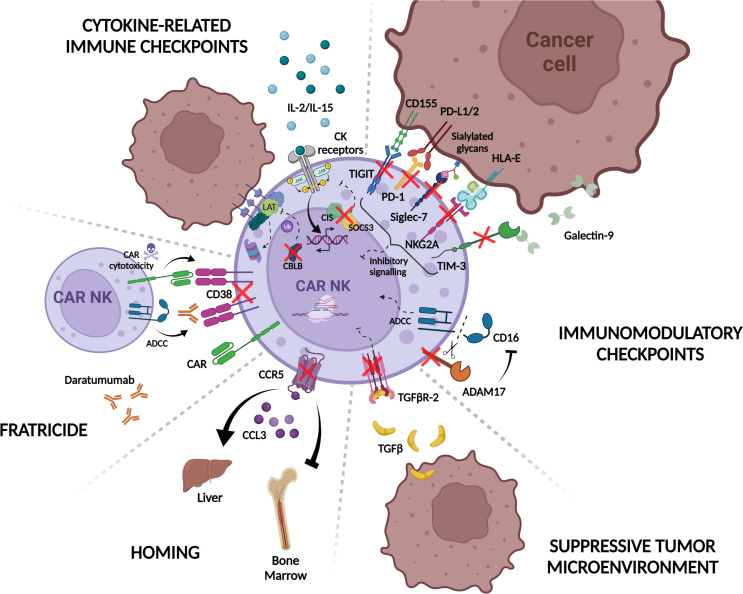
Figure 4.
CRISPR/Cas9 knock-out strategies to improve CAR-NK immunotherapy. CAR-NK function and cytotoxicity are modulated by intrinsic mechanisms in NK cells. For example, engagement of tumor ligands with NK immunomodulatory checkpoint receptors such as TIGIT, PD-1, NKG2A, TIM-3, and Siglec-7, inhibit CAR-NK cell response to target cells. ADAM17 also restrains NK cell ADCC response by shedding CD16 receptor from the NK cell surface. Additionally, in response to cytokine signaling, the expression of internal checkpoints including CLBL, SOCS3, and CIS regulate NK activation and immune synapsis formation with tumor cells. The suppressive tumor microenvironment contributes as well to CAR-NK inhibition through the release of suppressive factors like TGF-β. In this context, CAR-NK potency is attenuated and less effective against tumor cells. CAR-NK cell homing is also regulated by chemokine receptors such as CCR5 that mediates homing to the liver in response to CCL3 reducing CAR-NK efficacy against bone marrow-resident tumors. Another problem that CAR-NK manufacturing can encounter is fratricide either by expression of the CAR-targeted molecule on the surface of the effector cell or the use of monoclonal antibodies that bind to NK cells and induce “self-killing” through ADCC. Ablation of different NK cell proteins implicated in these pathways by the use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system (red crosses) would overcome the aforementioned limitations and result in more potent, persistent, and tumor-directed CAR-NK effectors for their use in adoptive immunotherapy. PD-1, Programmed Death 1; TIGIT, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; NKG2A, natural killer group 2A; PD-L1/2, Programmed Death ligand-1/2; HLA-E, HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, alpha chain E; ADAM-17, A disintegrin and metalloprotease 17; TGF- β, Transforming growth factor beta; TGFβR-2, Transforming growth factor beta receptor type 2; CCL3 Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3; CCR5, C-C chemokine receptor type 5; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; ADCC, Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; CK, cytokines; CIS, cytokine-inducible SH2-containing protein; SOCS3, suppressors of cytokine signaling; LAT, linker for activation of T cell; CBLB, Casitas B-lineage lymphoma protooncogene B Created with BioRender.com.