Extended Data Figure 2: Extended BCR repertoire data.
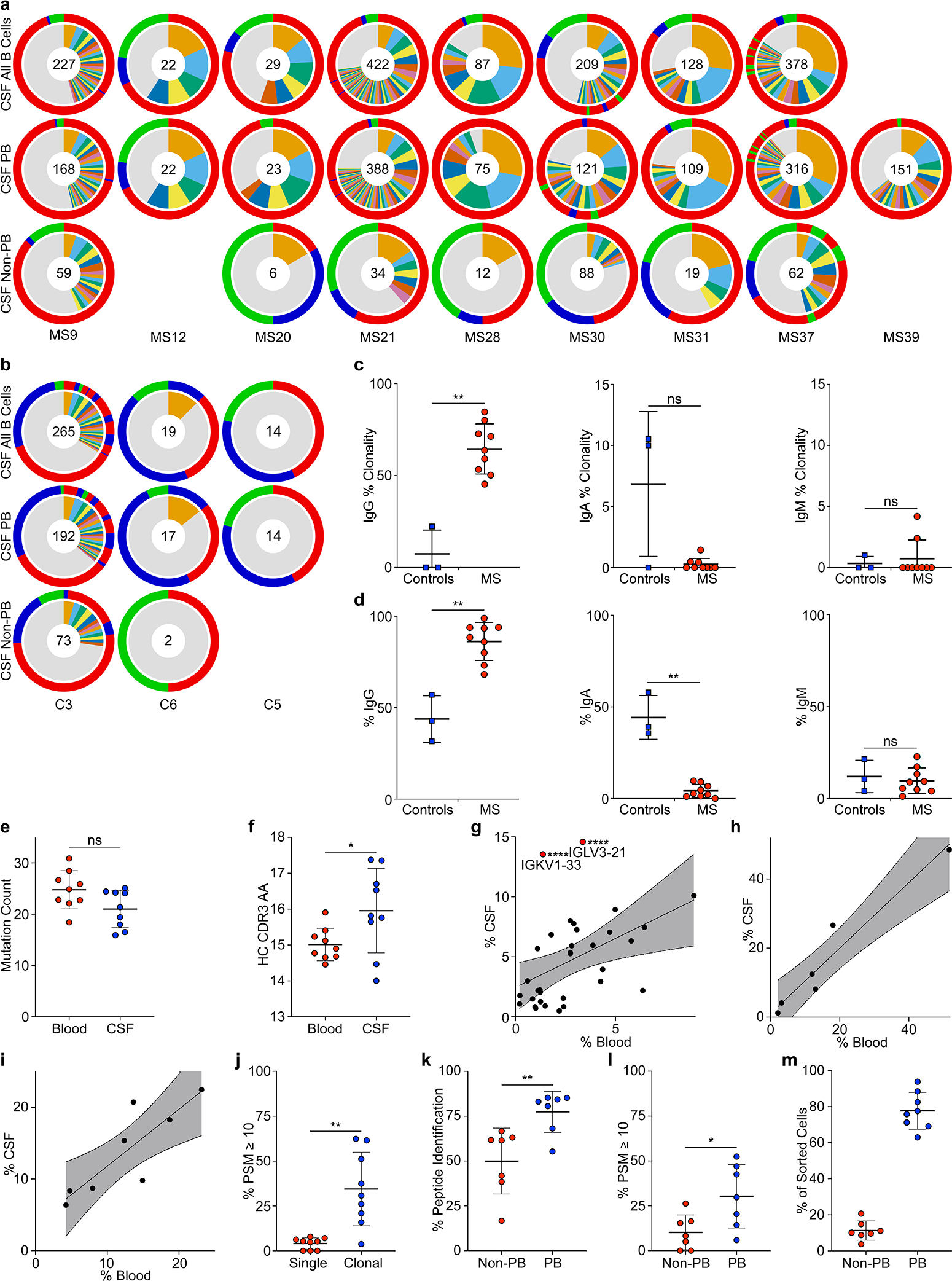
a-i, Single-cell BCR repertoire sequencing data, a, individual repertoires from all CSF B cells (top row) and subdivided into CSF plasmablasts (middle row) and non-plasmablast B cells (bottom row) of n=9 MS patients. b, Individual repertoires of all CSF B cells (top row) and subdivided into CSF plasmablasts (middle row) and non-plasmablast B cells (bottom row) of n=3 control patients. Numbers indicate number of sequences, inner circle: colored wedges represent clonal expansions and grey area represents singleton antibody sequences, outer circle: immunoglobulin classes, red: IgG, blue: IgA, green: IgM, sequence locations in outer circle correspond to inner circle. No non-plasmablast B cells were sorted for MS12 and C5. Only plasmablasts were sorted for MS39. c, Clonality, percent of clonal sequences in CSF B cells are shown, comparing BCR repertoires of control patients (n=3) to MS patients (n=9). Data corresponds to data shown in (Fig. 1b) and is separated into immunoglobulin classes IgG (left), IgA (center), and IgM (right). Means ± SD of individuals’ repertoires are shown. d, Immunoglobulin class distribution, percent of IgG (left), IgA (center), and IgM (right) of all CSF B cells are shown for n=3 control patients and n=9 MS patients. Means ± SD of individuals’ repertoires are shown. e, IGHV and IGLV cumulated mutation count in plasmablasts in blood (red) vs. CSF (blue), means ± SD of n=9 patients samples. f, Mean HC CDR3 lengths (amino acid sequences) of plasmablasts in blood (red) vs. CSF (blue), means ± SD of n=9 patient samples. g-i, Immunoglobulin gene distribution in blood vs. CSF plasmablasts for g, IGLV, IGKV1–33, ****P < 10−6, IGLV3–21, ****P = 3×10−6 according to unpaired two-tailed Student’s t tests, Holm-Sidak adjusted for multiple comparisons, h, IGHJ, and i, IGLJ. Each dot represents the usage of one gene across n=9 MS patient repertoires in the respective compartments. Linear regression lines and 95% confidence interval are shown. j, Mass spectrometry data of purified CSF immunoglobulins, showing variable chain sequences that could be uniquely identified in singleton BCR sequences vs. plasmablast sequences, peptide-spectral matches (PSM) cutoff ≥10, means ± SD of n=9 MS patients, **P = 0.0012. k,l, Same mass spectrometry data set as in (j), showing variable chain sequences that could be uniquely identified in non-plasmablast BCR sequences vs. plasmablast sequences, means ± SD of n=7 MS patients, k, PSM cutoff ≥1, **P = 0.007, l, PSM cutoff ≥10, *P = 0.037. l, m, Single-cell sequencing efficacy in non-plasmablast B cells (red) vs. plasmablasts (blue) in CSF. Fraction of sequences that passed filter thresholds are shown as percentages of the number of sorted cells in the respective group, means ± SD of n=8 patient samples (no non-PB value for MS39). c,d,j-l, P according to unpaired two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. d-i, P according to unpaired two-sided Student’s t-test. Immunoglobulin heavy V gene, IGHV; Immunoglobulin heavy J gene, IGHJ; Immunoglobulin light V gene, IGLV; Immunoglobulin light J gene, IGLJ; peptide-spectral matches, PSM.
