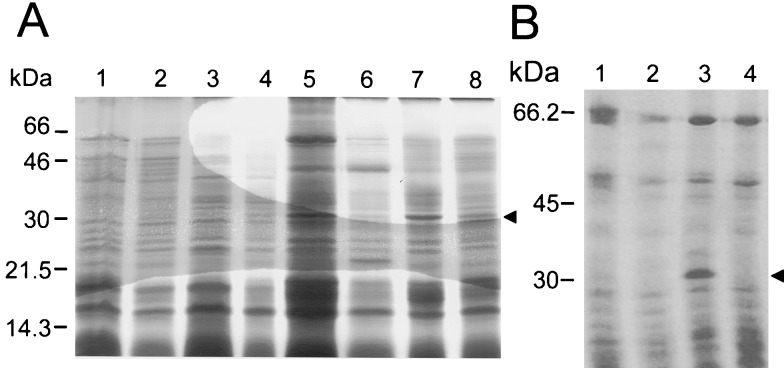
FIG. 2.
Extraction of TasA from gerE mutant spores. Spores of a wild-type strain and various mutant strains were purified, and the coat proteins were extracted by treatment with a buffer containing SDS-DTT (A) or with alkali (B). The extracted proteins were resolved in 12.5% polyacrylamide gels containing SDS, and the gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. The spores used for the extraction of the coat proteins were as follows: (A) lane 1, wild type; lane 2, tasA mutant; lane 3, cotE mutant; lane 4, cotE tasA mutant; lane 5, gerE mutant; lane 6, gerE tasA mutant; lane 7, cotE gerE mutant; lane 8, gerE cotE tasA mutant; (B) lane 1, wild type; 2, tasA mutant; lane 3, gerE mutant; lane 4, gerE tasA mutant. The arrowheads indicate the position of the 30-kDa TasA polypeptide which is readily extracted from gerE mutant spores. Also indicated are the positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons).