FIG. 6.
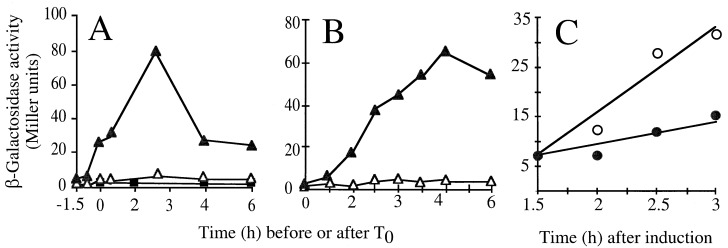
tasA is controlled by ςH. The figure illustrates the time course of β-galactosidase production by various strains bearing a tasA-lacZ transcriptional fusion integrated at the tasA locus. Different growth conditions were used. (A) Strains were induced to sporulate in DSM, and T0 defines the onset of sporulation. (B) YT medium (2×) was used (T0 corresponds to an OD600 of about 0.3, whereas maximum enzyme activity was reached about 3 to 4 h later). Enzyme production was measured in strain AZ404 (tasA-lacZ) (dark triangles) and its congenic sigH mutant (AZ393, dark squares). (C) A Pspac-spo0H strain carrying the tasA-lacZ fusion was grown in 2× YT medium to a low OD600 value (about 0.2), at which point the culture was divided in half. IPTG was added to one flask (open circles) but not to the other (closed circles). Samples were collected at the indicated times, and the specific activity of β-galactosidase was determined with the substrate o-nitrophenol-β-d-galactopyranoside (ONPG). Background levels of β-galactosidase synthesis were estimated for the wild-type strain PY79 (open triangles in panels A and B).