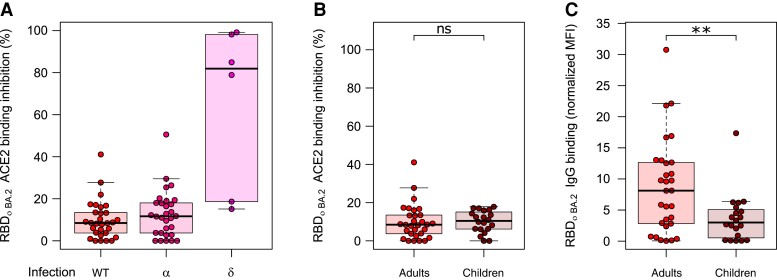
Figure 5.
Differences in immunoglobulin G (IgG) binding response and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binding inhibition toward BA.2 among different populations of convalescent samples. Comparative ACE2 binding inhibition (A and B) and IgG binding capacity (C) between convalescent samples from different pandemic waves (A) and adults and children (B and C) for BA.2. A, There are no differences in ACE2 binding inhibition toward BA.2 for individuals infected with wild-type (WT) (n = 30), Alpha (n = 30), or Delta (n = 6). B, Children (n = 20) and adults (n = 30) have similar ACE2 binding inhibition toward BA.2 following WT infection, although they have significantly reduced IgG binding capacity (P = .01). C, Boxes represent the median with 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers show the largest and smallest nonoutlier values. Outliers were determined by 1.5 interquartile range. Statistical significance was calculated by Mann–Whitney U test: **P < .01; ns, P < .05. The equivalent data for BA.1 are provided as Supplementary Figure 4. Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; IgG, immunoglobulin G; MFI, median fluorescence intensity; RBD, receptor-binding domain; WT, wild-type.