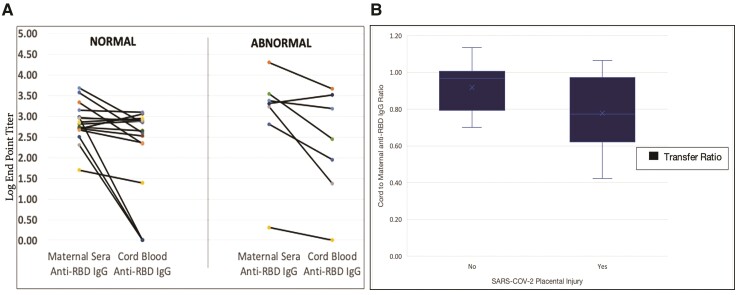
Figure 1.
(A)Absolute anti-receptor biding domain (RBD) immunoglobulin (Ig)G concentrations in cord blood compared with maternal sera according to presence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) placental injury. All maternal sera and 83% (n = 19) cord blood samples had detectable anti-RBD IgG. There was no statically significant difference in the absolute cord blood anti-RBD IgG concentrations in patients with and without SARS-CoV-2-induced placental injury (log end dilution titer 2.7 [interquartile range {IQR}, 1.8–3.6] vs 2.7 [IQR, 2.4–2.9], P = .59). (B) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD IgG cord-to-maternal ratios grouped according to presence of SARS-CoV-2 placental injury. The cord, maternal ratio, or transplacental transfer efficiency was calculated as the ratio between cord blood and maternal anti-RBD IgG log endpoint titers. The median antibody transfer efficiency in placentas without SARS-CoV-2-induced placental injury was 0.77 (IQR, 0.61–0.97). The median antibody transfer efficiency in placentas with SARS-CoV-2-induced placental injury was 0.97 (IQR, 0.80–1.01; P = .05).