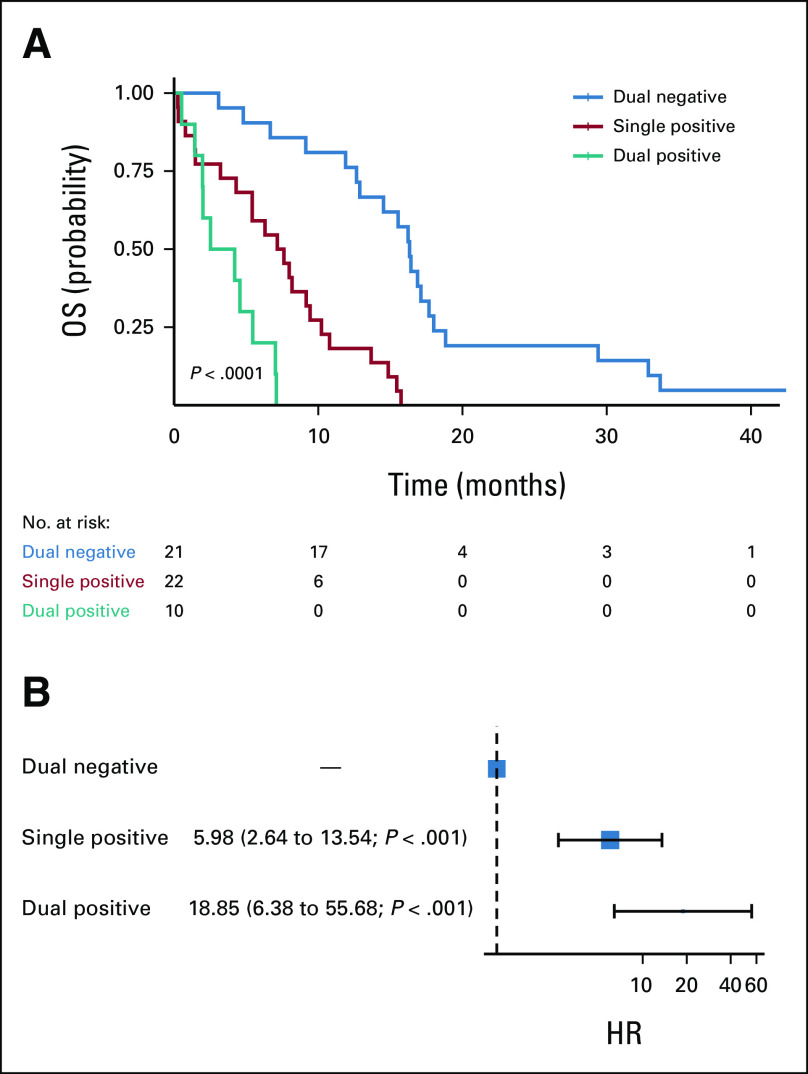
FIG 2.
Assessment of OS by CTC and ctKRAS status by (A) the Kaplan-Meier method in patients with mPDAC along with the number of patients at risk and (B) by univariate Cox proportional hazards modeling in patients with mPDAC. Patients were categorized as dual negative for CTCs and ctKRAS (CTCs < 1/mL and ctKRAS VAF < 0.05), single positive (CTCs ≥ 1/mL or ctKRAS VAF ≥ 0.05), or dual positive (CTCs ≥ 1/mL and ctKRAS VAF ≥ 0.05). Twenty-one patients with mPDAC were dual negative, 22 were single positive, and 10 were dual positive. Among patients with mPDAC, dual positivity was associated with worse OS than dual negativity (HR, 18.84; 95% CI, 6.38 to 55.68; P < .001) and single positivity was associated with worse OS than dual negativity (HR, 5.98; 95% CI, 2.64 to 13.54; P < .001). CTC, circulating tumor cell; ctKRAS, circulating tumor KRAS; HR, hazard ratio; mPDAC, metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; OS, overall survival; VAF, variant allele fraction.