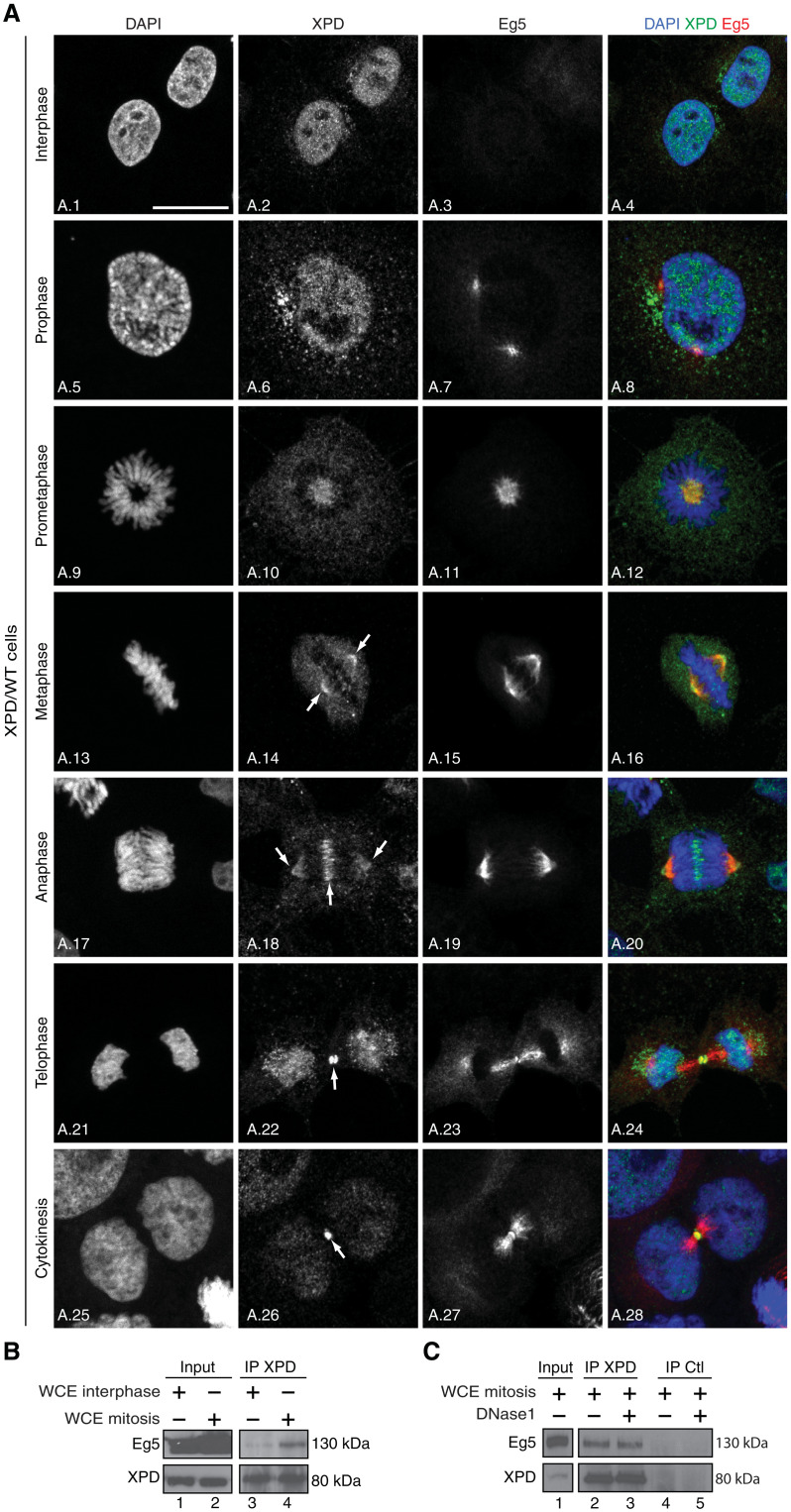
Fig. 1. XPD colocalizes and interacts with Eg5.
(A) Immunofluorescence analysis of XPD and Eg5 during interphase and different mitotic phases. Human XPD/WT cells were synchronized by double thymidine block and release, collected 9 hours after release, and analyzed by confocal microscopy at interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase/cytokinesis. The arrows point to the localization of XPD at the mitotic spindle, the midzone, and at the midbody. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Whole-cell extracts (WCEs) were isolated from XPD/WT cells in interphase and mitosis (cells were treated 16 hours with nocodazole and collected 90 min after nocodazole release). After immunoprecipitation with anti-XPD (IP XPD), the coimmunoprecipitated proteins were resolved by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and blotted with anti-XPD and anti-Eg5. The results are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Whole-cell extracts were isolated from XPD/WT cells in mitosis [as indicated (B)], treated (when indicated, +) with deoxyribonuclease 1 (DNase1) (5 μg), and incubated (16 hours, 4°C) with anti-XPD (IP XPD) or irrelevant immunoglobulin G (IgG; IP Ctl) bound to magnetic beads. After washes, the coimmunoprecipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted with anti-XPD and Eg5. The results are representative of two independent experiments.