Fig. 5.
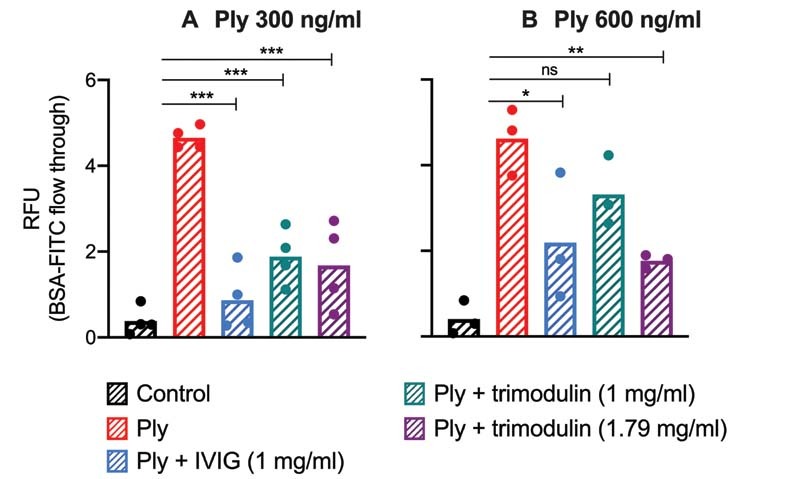
Platelet's pore sealing capacity upon pneumolysin treatment. The pore sealing capacity of platelets upon treatment with different pneumolysin concentrations ( A, B ) or with pneumolysin preincubated with IVIG or trimodulin, respectively, was assessed by their capability to inhibit BSA-FITC diffusion through a perforated fibronectin-coated membrane. BSA-FITC diffusion was quantified by the measurement of relative fluorescence units (RFU). Bars represent the mean of platelets of at least three donors. As a control, platelets were incubated with PBS only. Statistical analysis was performed using the Shapiro–Wilk normality test and repeated measures one-way ANOVA. A p -value <0.05 was considered to be significant ( * > 0.033, ** > 0.002 , *** > 0.001). ANOVA, analysis of variance.
