Figure 1.
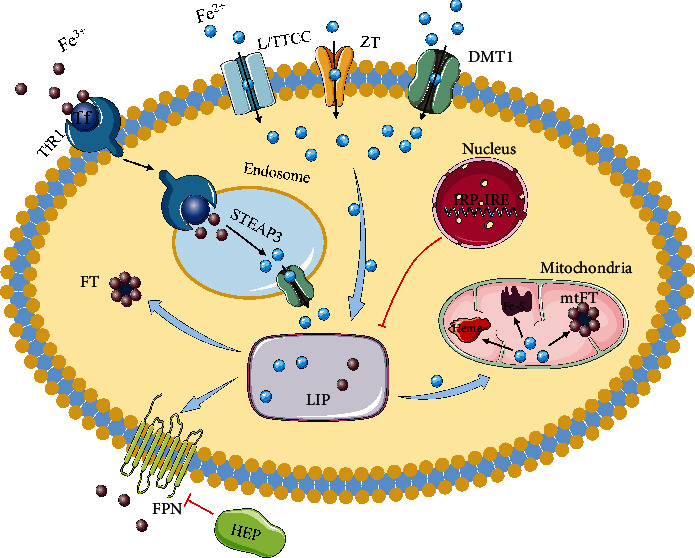
Iron homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. TBI enters cardiomyocytes via TfR1. TBI is reduced to Fe2+ by STEAP3 after release in the endosome, and Fe2+ is transferred to the cytoplasm by DMT1. NTBI enters via DMT1, LTCC, TTCC, and ZT. After entering the CMs, iron becomes part of the LIP and works through different pathways. A portion of iron is used by mitochondria to produce heme and Fe-S, and a portion is stored in FT. Furthermore, another part of iron is exported through the FPN and regulated by HEP. And cardiac iron homeostasis is regulated by IRP-IRE. TBI: Tf-bound iron; NTBI: non-Tf-bound iron; TfR1: transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3: six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; DMT1: divalent metal transporter 1; LTCC: L-type calcium channel; TTCC: T-type calcium channel; ZT: zinc transporters; LIP: labile iron pool; FT: ferritin; FPN: ferroportin; Fe-S: iron–sulfur cluster; mtFT: mitochondrial ferritin; HEP: hepcidin; IRE: iron-responsive elements; IRP: iron regulatory protein.
