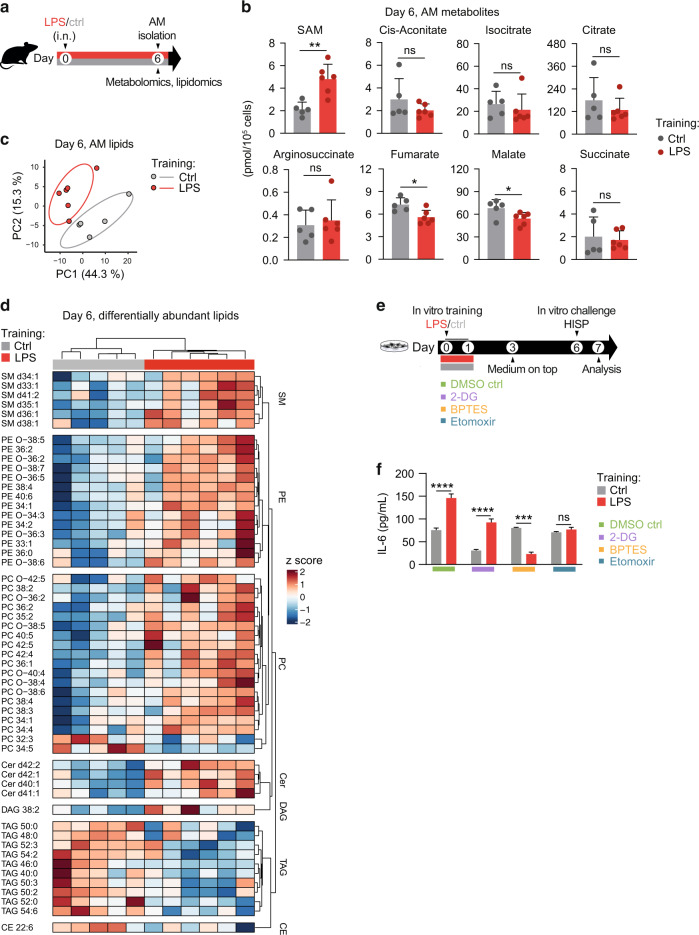
Fig. 5. LPS-induced metabolic activation contributes to the establishment of AM memory.
a Experimental setup for metabolomic/lipidomic analyses of AMs on day six after in vivo training with LPS/saline. b AM intracellular metabolites related to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. SAM: S-adenosyl-methionine. c Principal component analysis of centered log-ratio transformed AM lipidomics data. d Heatmap displaying differentially abundant lipids (FDR 0.2, p-value ≤ 0.05) of trained and control AMs. Metabolomic/lipidomic analyses were performed with 5-6 biological replicates per group. Cer ceramides; DAG diacylglycerols; PE phosphatidylethanolamines; SM sphingomyelins; PC phosphatidylcholines; CE cholesterol esters; TAG triacylglycerols. e Experimental setup for mexAM training with LPS or medium in presence of indicated metabolic inhibitors or DMSO, followed by in vitro HISP challenge (16 h) six days later. f IL-6 levels of mexAMs stimulated as described in e. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Graphs show means + SD of 5-6 biological replicates (b) or means + SEM of 4-5 technical replicates (f). Statistical analysis: student’s t-test (b) and two-way ANOVA (f) (factor 1: training; factor 2: inhibitor). ns, not significant. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.