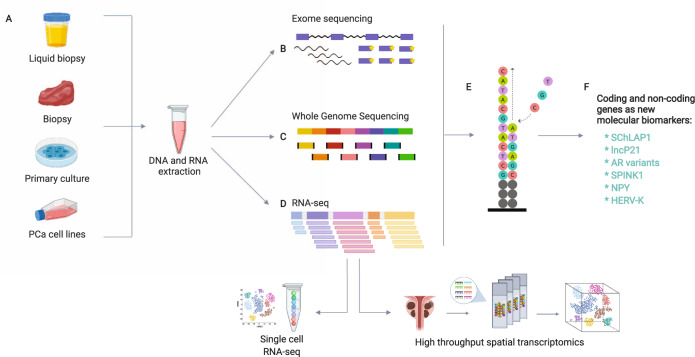
Fig. 2. Basic research towards the discovery of new molecular biomarkers.
There are several sources and molecular approaches for the detection of new biomarkers in PCa. A This can be achieved by using an in vivo model -for which a prostate biopsy should be taken-, a primary culture or a PCa cell line. B Exome sequencing. The DNA samples are first fragmented and then biotinylated oligonucleotide probes -also known as baits- are used to selectively hybridize to target regions in the genome. C Whole-Genome Sequencing. This sequencing technique allows a uniform coverage across the complete genome. D RNA-Seq. RNA samples are synthesized into cDNA once it has been fragmented. Then, adaptors are attached to both ends of each fragment so they can be amplificated by PCR and subsequently sequenced [122]. Within the variants of this technique can be found single-cell RNA-seq, total RNA-seq, targeted RNA-seq, small RNA-seq, spatial transcriptomics, poly-A enrichment, ribosomal RNA depletion, among others. E Illumina next-generation sequencing technology: Individual DNA or cDNA molecules are placed on a flowcell for sequencing by synthesis by using fluorescent labeled nucleotides. PacBio sequencer and Nanopore sequencer can read more than 100 Kb in length of DNA, as well as the disposable sequencer MinION which doesn’t need prior installation [123]. F After a bioinformatic data analysis the results of the sequencing provide new genes as biomarkers candidates in PCa.