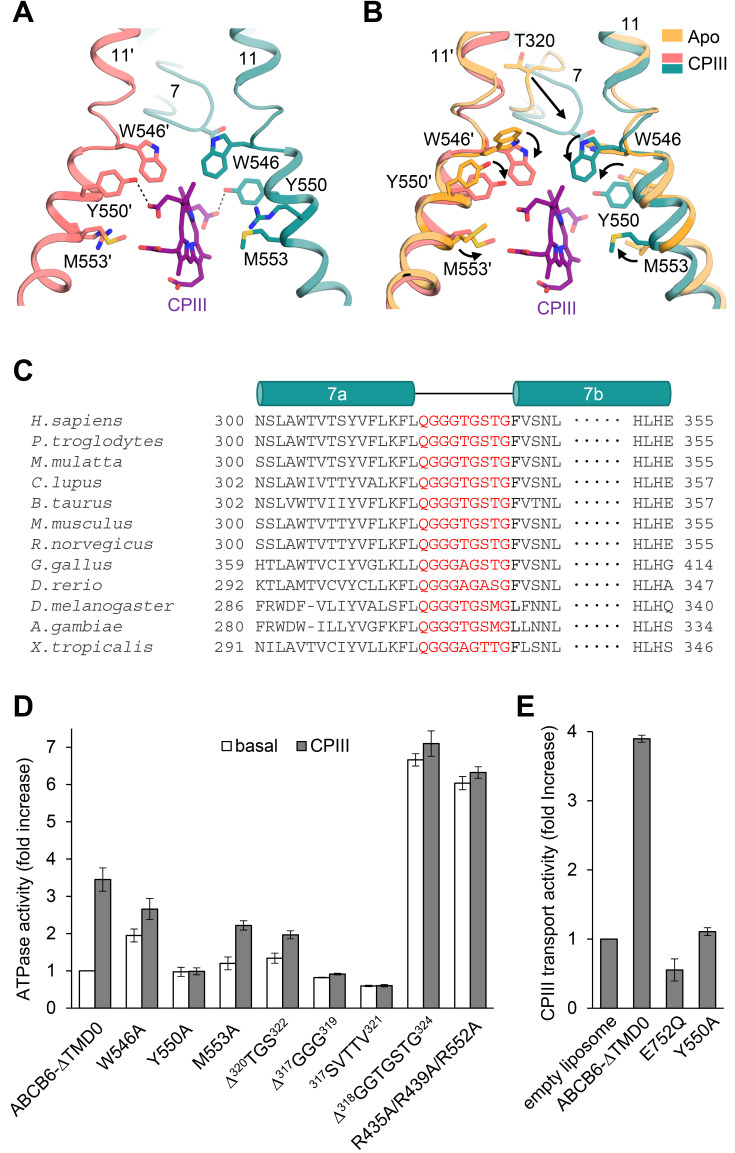
Fig. 3. Close-up view of the CPIII-bound site.
(A) The view is rotated by 105 degrees along the vertical axis from Fig. 2B. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds between CPIII and Y550. (B) Structure comparison of the substrate binding sites with and without CPIII. Structural changes are marked by black arrows. (C) Sequence alignments of TM 7 of the human ABCB6 homologues. The residues in the TM 7 bulge loop are highlighted in red. (D) ATPase activities of various mutants with 100 µM CPIII. The basal activity of ABCB6-∆TMD0 is set to 100%. Values are mean ± SD of three replicates. (E) CPIII transport activities of the ABCB6-∆TMD0 and other mutants in liposomes. The ATPase-defective mutant E752Q was used as a negative control. Data for protein-free liposomes in the presence of 200 µM CPIII and 2 mM ATP was taken as 100%. Values represent the mean ± SD of triplicate measurements.