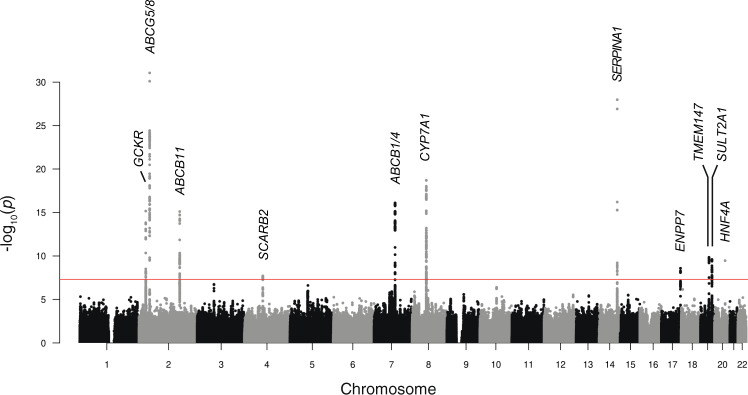
Fig. 1. Manhattan plot for the genome-wide association study meta-analysis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP).
Data shown are from the combined meta-analysis including 1138 cases and 153,642 controls, all of European ancestry. The chromosomes are ordered on the x axis; the y axis shows the −log10(P) values for the association tests. Eleven loci achieved genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10−8, indicated by the red line). The prioritized gene at each locus is shown. The effector gene functional prioritization strategy followed in this study is presented in Fig. 2. Association testing was performed using a generalized logistic mixed model to account for population stratification and saddle-point approximation to control for type 1 error rates due to unbalanced case–control ratios, followed by meta-analysis weighting the effect size estimates using the inverse of the standard errors.