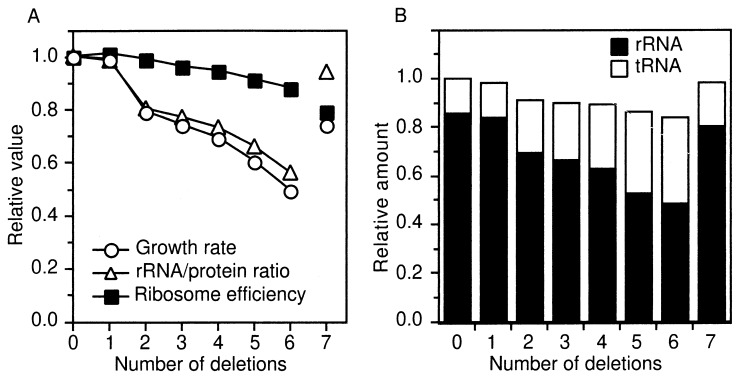
FIG. 5.
Physiological effects of rrn inactivation. (A) Relative growth rates, rRNA/protein ratios, and ribosome efficiencies. Growth rates (doublings per hour) were determined by monitoring the turbidity of each culture with a Klett-Summerson photoelectric colorimeter and are presented relative to the rrn+ strain values. The maximum standard error of growth rate measurements was 0.07. The actual growth rate of the rrn+ strain, TA563, was 2.0 doublings/h. rRNA/protein ratios were determined from the data presented in panel B. Ribosome efficiencies were calculated from growth rates and rRNA/protein ratios as described by Bremer and Dennis (5). (B) Relative total RNA/total protein and tRNA/rRNA ratios. The total RNA/total protein and tRNA/rRNA ratios in each total RNA sample were determined as described previously (1). These parameters were normalized to the total amount of RNA in the rrn+ strain. Closed and open bars represent the amounts of rRNA and tRNA, respectively. The maximum standard error of RNA measurements was 0.05. Note that the Δ6 strain contains only the tRNA plasmid while the Δ7 strain contains both the tRNA and rRNA plasmids.